Emerging Trends in Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is no longer just a futuristic concept — it’s actively transforming industries today. However, the AI landscape is dynamic, and new trends continue to emerge that are pushing the boundaries of what machines can do. Below is an in-depth exploration of these trends.
1. Generative AI: Revolutionizing Content Creation
Generative AI involves models trained to produce new content — whether it be text, images, code, or even music.
- How it works: It uses deep learning models, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformer models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformers).
- Popular Tools:
- ChatGPT & Gemini (text and code generation)
- MidJourney & DALL·E (art and image creation)
- ElevenLabs (AI voice cloning)
- Impact Areas:
- Marketing: AI can now generate blog posts, ad copies, and social media content in seconds.
- Entertainment: Movies are using AI for scriptwriting and visual effects.
- Education: AI generates personalized study materials and quizzes.
Case Study: Coca-Cola used OpenAI's DALL·E and GPT models in their "Create Real Magic" campaign, where users generated custom branded art.
2. MLOps (Machine Learning Operations): Scaling AI for Business
MLOps is an engineering practice that helps organizations manage ML models efficiently throughout their lifecycle.
- Why it matters:
- AI models need continuous updates and monitoring to perform well in real-world settings.
- It solves the “production gap” — where models work in labs but fail in real-world applications.
- Key Practices:
- Version control for datasets and models
- Automated testing and deployment
- Monitoring for performance drift
- Tools: MLFlow, Kubeflow, and Amazon SageMaker
Case Study: Netflix uses MLOps to manage the constant retraining and deployment of its recommendation engine models.
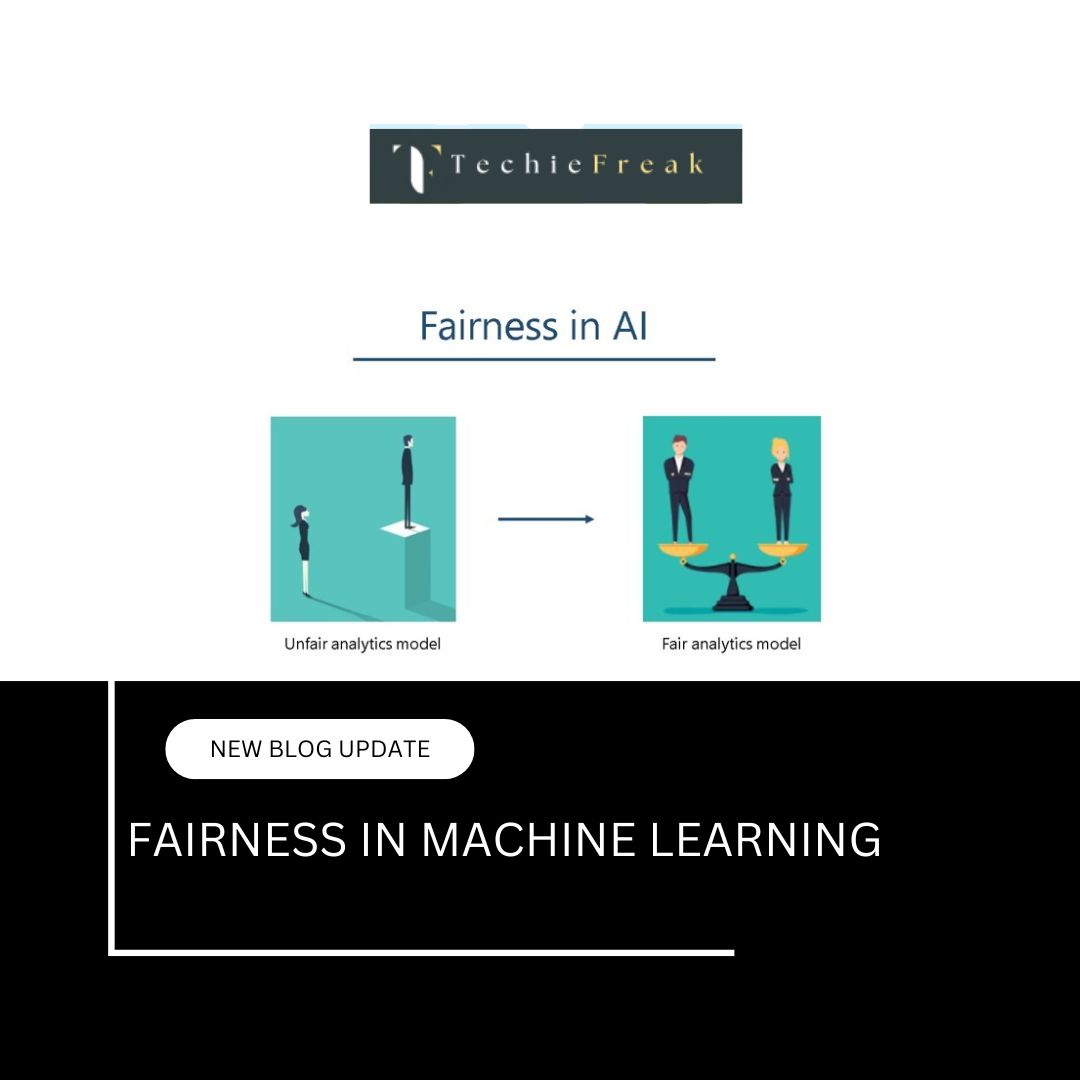
3. Explainable AI (XAI): Making AI Transparent
As AI starts making critical decisions in healthcare, finance, and law, explainability has become crucial.
- Why it’s needed:
- Builds trust in AI systems among users.
- Essential for legal compliance (e.g., GDPR’s "right to explanation").
- Detects biases in model outputs.
- Methods:
- LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations)
- SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations)
- Real-World Use:
- Banks using XAI to explain loan approval or rejection decisions.
- Hospitals ensuring AI diagnoses can be reviewed by doctors.
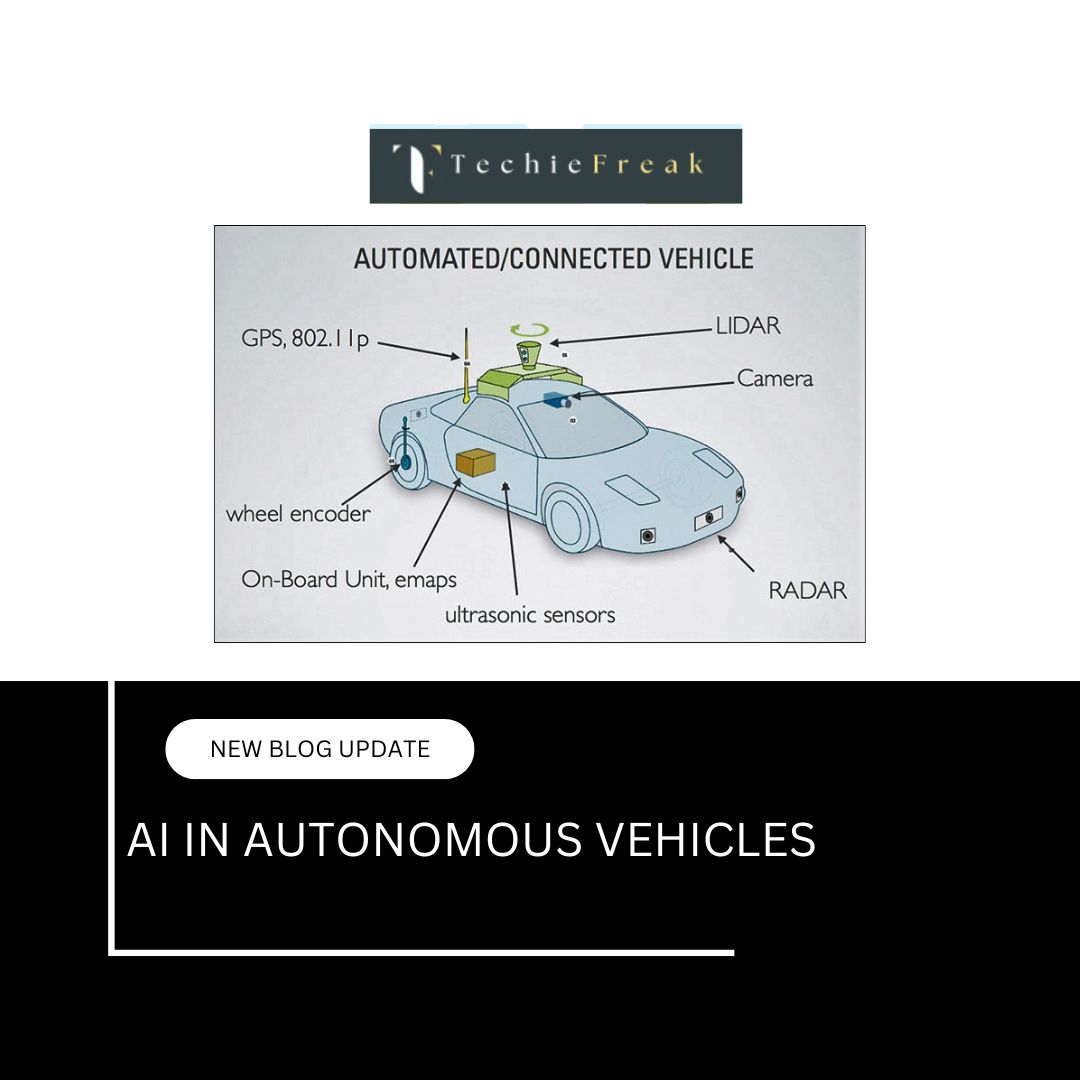
4. AI at the Edge: Real-Time Intelligence
Edge AI refers to running AI algorithms on devices close to the data source (edge devices) rather than sending data to the cloud.
- Advantages:
- Reduced Latency: Critical for autonomous vehicles and real-time surveillance.
- Privacy: Data stays local, enhancing security.
- Offline Functionality: Works even without internet connectivity.
- Use Cases:
- Smartphones (face recognition, voice assistants)
- Drones (object detection)
- Industrial IoT devices (predictive maintenance)
Case Study: Tesla cars process AI algorithms on board for real-time driving decisions without relying on cloud servers.
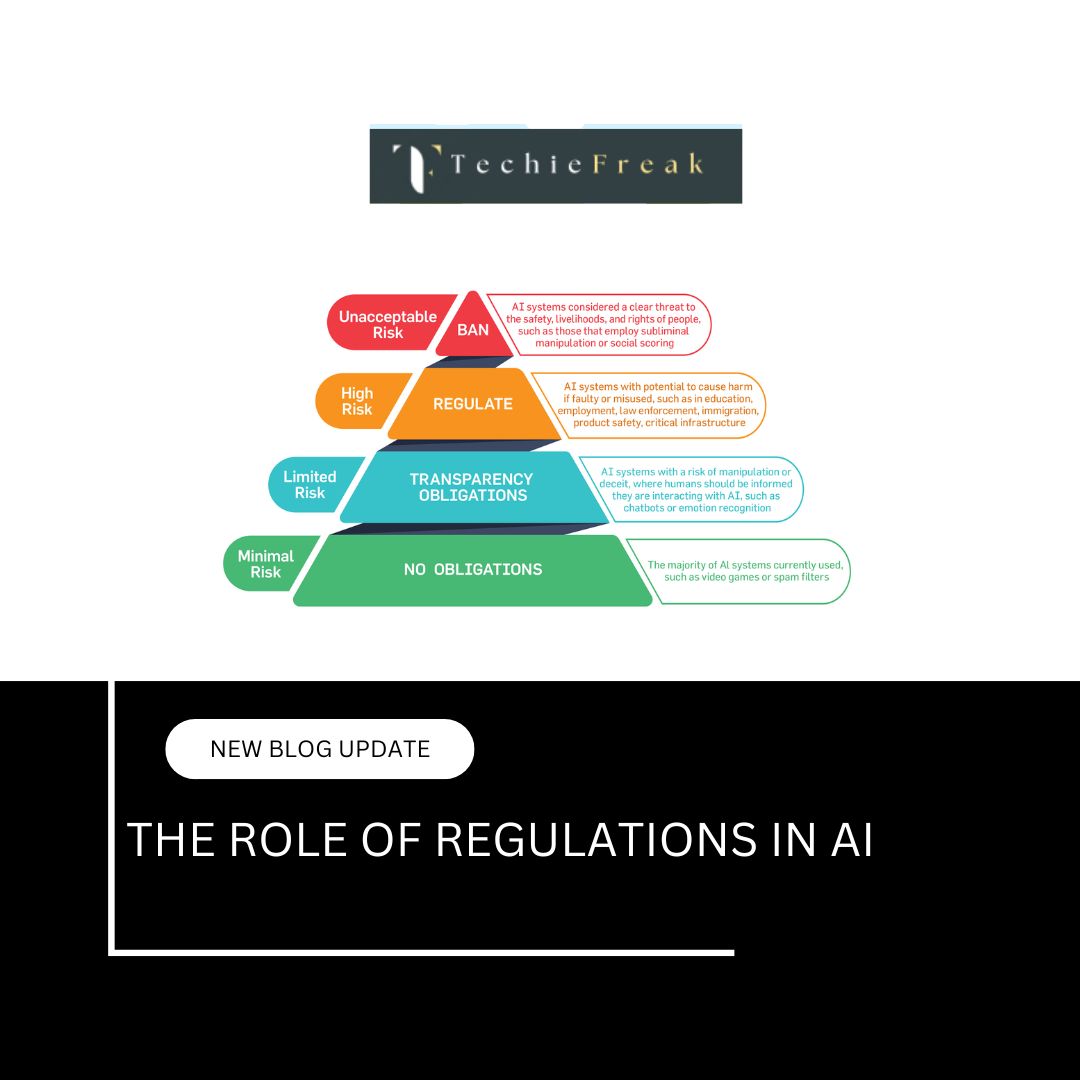
5. Ethical AI and Governance: Keeping AI Fair
With AI’s power comes the risk of misuse, bias, and ethical concerns.
- Key Concerns:
- Bias in algorithms leading to discrimination (e.g., hiring systems favoring certain genders or races).
- Surveillance misuse violating privacy rights.
- Deepfakes causing misinformation.
- Governance Initiatives:
- European Union’s AI Act classifies AI systems based on risk levels.
- Companies forming AI Ethics Committees (e.g., Google, Microsoft).
- Best Practices:
- Bias audits
- Inclusive dataset collection
- Transparency reporting
6. AI-Driven Hyperautomation: Beyond Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Hyperautomation combines AI with RPA to automate complex business processes, including those involving decision-making.
- Examples:
- Chatbots answering customer queries with human-like responses.
- AI HR systems shortlisting resumes based on job descriptions.
- AI financial tools automating risk assessments.
- Benefits:
- Cuts down operational costs
- Speeds up workflows
- Reduces manual errors
Case Study: IBM's Watson AI helps automate insurance claims processing, significantly reducing turnaround time.
7. Multimodal AI: Breaking the Single-Modality Barrier
Multimodal AI models can understand and generate across multiple types of data — text, images, audio, and video.
- Popular Models:
- GPT-4 (can process text and images)
- Google Gemini (handles text, images, audio, and video)
- Applications:
- Virtual assistants that see (camera input) and hear (audio input) to respond intelligently.
- Healthcare AI that analyzes both medical reports and X-ray images for diagnosis.
- E-commerce: Virtual try-on systems using camera input and recommendation engines.
8. AI in Cybersecurity: Smart Defense Systems
Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, and AI is now essential for defense.
- Functions of AI in Security:
- Threat detection by recognizing unusual behavior patterns.
- Predictive analytics to foresee potential attacks.
- Automating incident response.
- Tools:
- Darktrace uses AI to detect cybersecurity threats in real-time.
- CrowdStrike Falcon platform uses ML for endpoint protection.
Case Study: Microsoft uses AI across its Azure platform to protect 1.3 billion devices globally.
9. AI-Powered Personalization: Tailoring Experiences
AI enables businesses to deliver personalized services by analyzing user data and predicting preferences.
- Industries Using This:
- E-commerce: Amazon recommends products.
- Streaming: Netflix suggests shows based on your watch history.
- Healthcare: Personalized treatment plans based on patient data.
- Techniques:
- Collaborative filtering
- Deep learning-based recommendation engines
10. Human-AI Collaboration: Augmenting, Not Replacing
The new wave of AI is designed to assist humans, not substitute them.
- How it works:
- AI handles repetitive, data-heavy tasks.
- Humans focus on creative, strategic, and emotional intelligence tasks.
- Real-World Pairings:
- Doctors using AI tools to cross-check diagnoses.
- Writers using AI to generate drafts and then refining the content.
- Architects using AI for initial designs which are later modified.
Case Study: In radiology, AI tools assist in early detection of tumors, but final reports are validated by human radiologists.
Conclusion
AI is advancing on multiple fronts — from generative models that create human-like content to edge AI enabling real-time decisions on devices. However, alongside growth comes the responsibility to ensure AI is explainable, ethical, and collaborative. Understanding these trends is key to preparing for the AI-driven world.




.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)