What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is a branch of computer science that enables machines to simulate human intelligence. This means machines can perform tasks that typically require human thinking, such as analyzing information, solving problems, learning from experiences, and making decisions.
For example, when you ask Siri or Google Assistant a question, it processes your voice, understands the intent, searches for an answer, and responds—mimicking human-like intelligence.
AI consists of multiple technologies that allow computers to think, learn, and act intelligently. It is often divided into three core functions:
1. Learning
AI systems gather large amounts of data and identify patterns. This learning process happens in three ways:
- Supervised Learning – The AI is trained using labeled data (e.g., teaching an AI to recognize cats by showing it thousands of cat images).
- Unsupervised Learning – The AI finds hidden patterns in data without predefined labels (e.g., AI clustering similar customer behaviors in marketing).
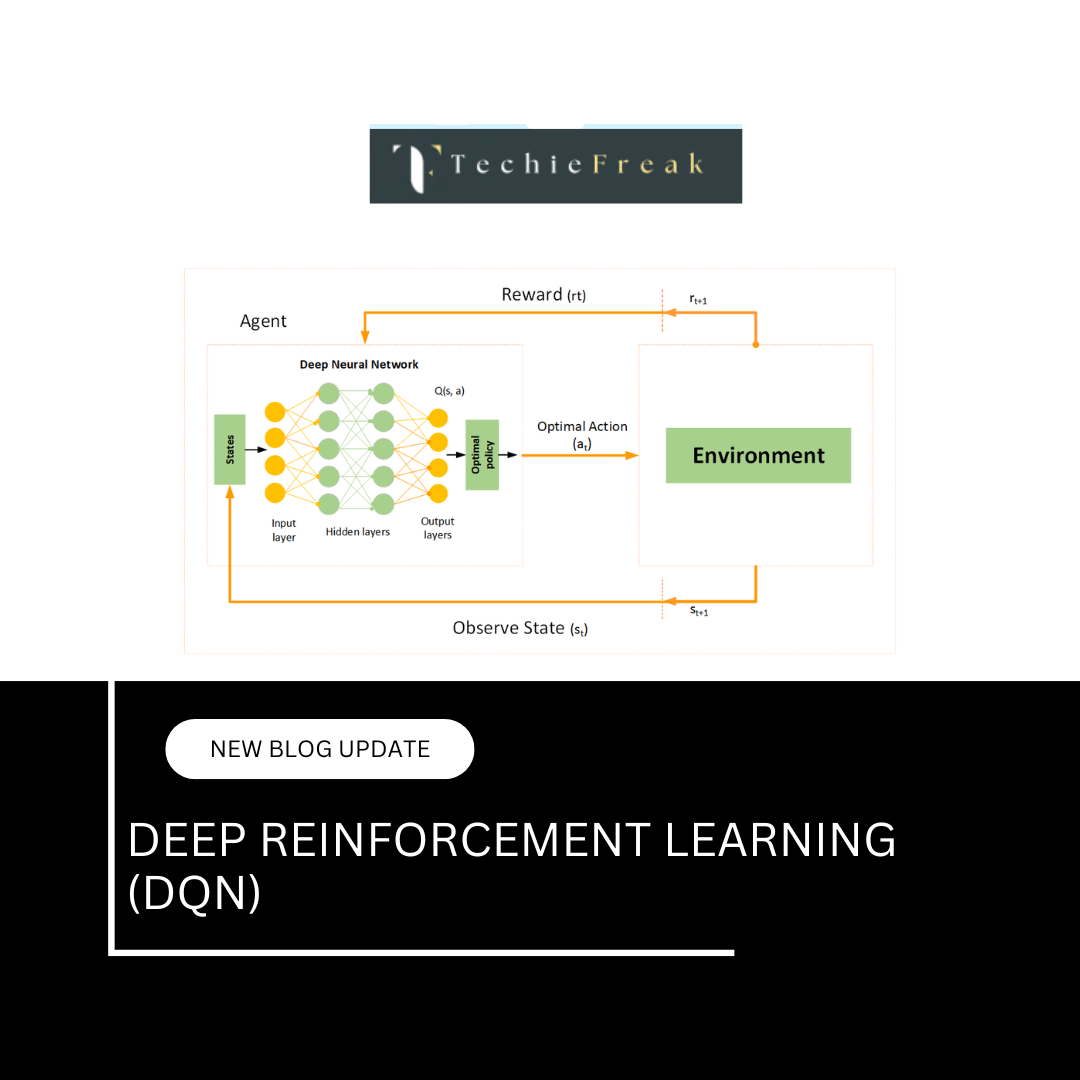
- Reinforcement Learning – The AI learns by trial and error, receiving rewards for correct actions (e.g., AI mastering chess by playing thousands of games).
2. Reasoning
AI applies logic to analyze data and draw conclusions. This allows it to:
- Solve complex problems (e.g., predicting stock market trends).
- Make decisions (e.g., self-driving cars choosing the safest route).
- Process and interpret natural language (e.g., chatbots understanding user queries).
3. Self-Correction
AI continuously improves its performance by analyzing mistakes and refining its algorithms. For example:
- Google’s search engine refines its ranking system based on what users click on.
- AI-powered grammar checkers improve over time by learning from user corrections.
How AI Works – A Detailed Explanation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) operates through a combination of advanced technologies and methodologies that enable machines to learn, reason, and make decisions. Below are some of the key components that power AI systems.
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data patterns and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following strict instructions, ML models recognize trends and make predictions based on previous experiences.
How Machine Learning Works:
ML involves three main approaches:
- Supervised Learning – The AI is trained using labeled data. Example: An AI trained on thousands of images of cats and dogs to correctly identify them.
- Unsupervised Learning – The AI finds patterns and relationships in data without predefined labels. Example: Grouping customers based on purchasing behavior in e-commerce.
- Reinforcement Learning – The AI learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for correct actions. Example: AI playing chess and improving by learning from past games.
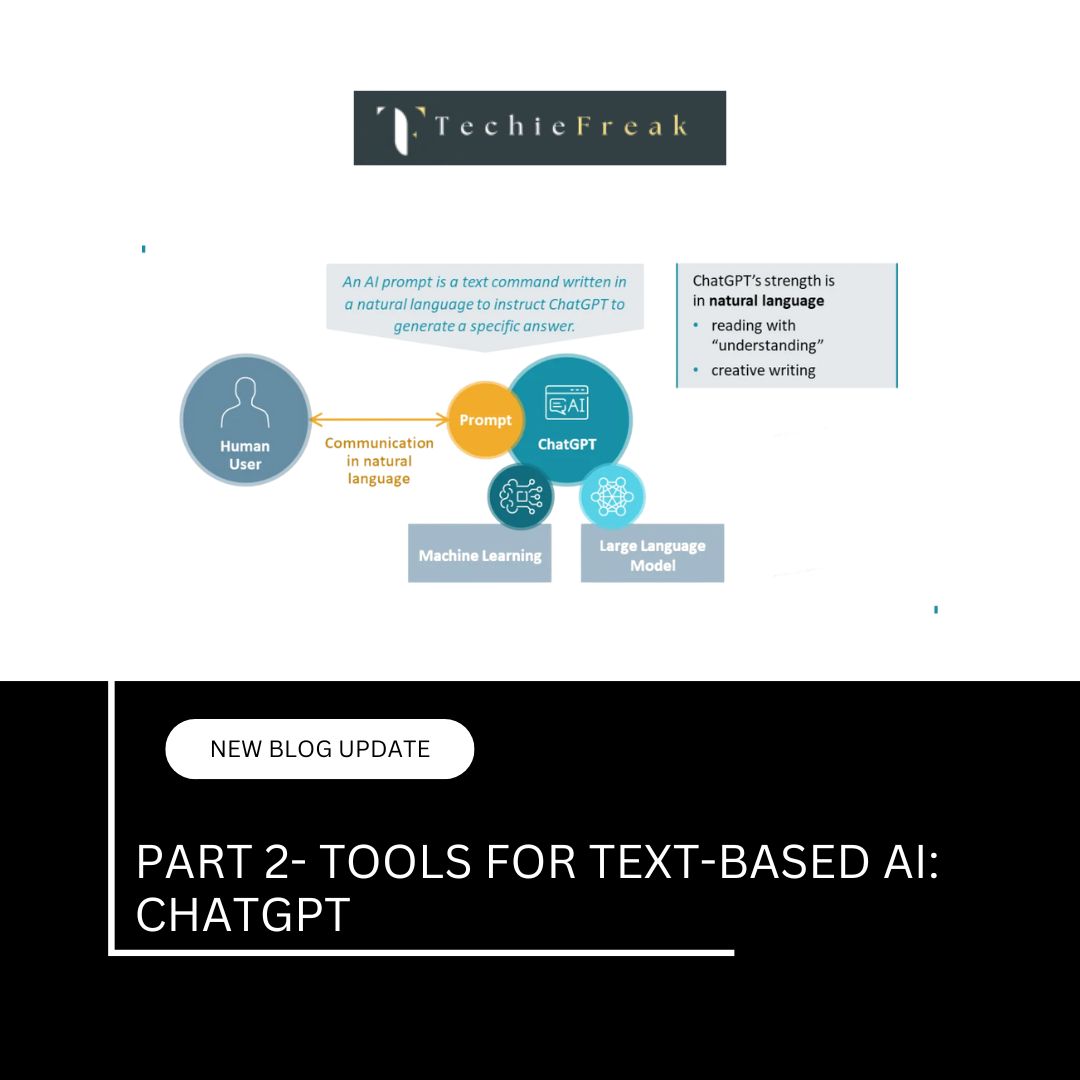
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language, allowing seamless interaction between humans and machines.
How NLP Works:
- Text Analysis – AI processes and understands human text, such as email spam detection.
- Speech Recognition – AI converts spoken words into text, used in voice assistants like Alexa and Siri.
- Machine Translation – AI translates text between languages, such as Google Translate.
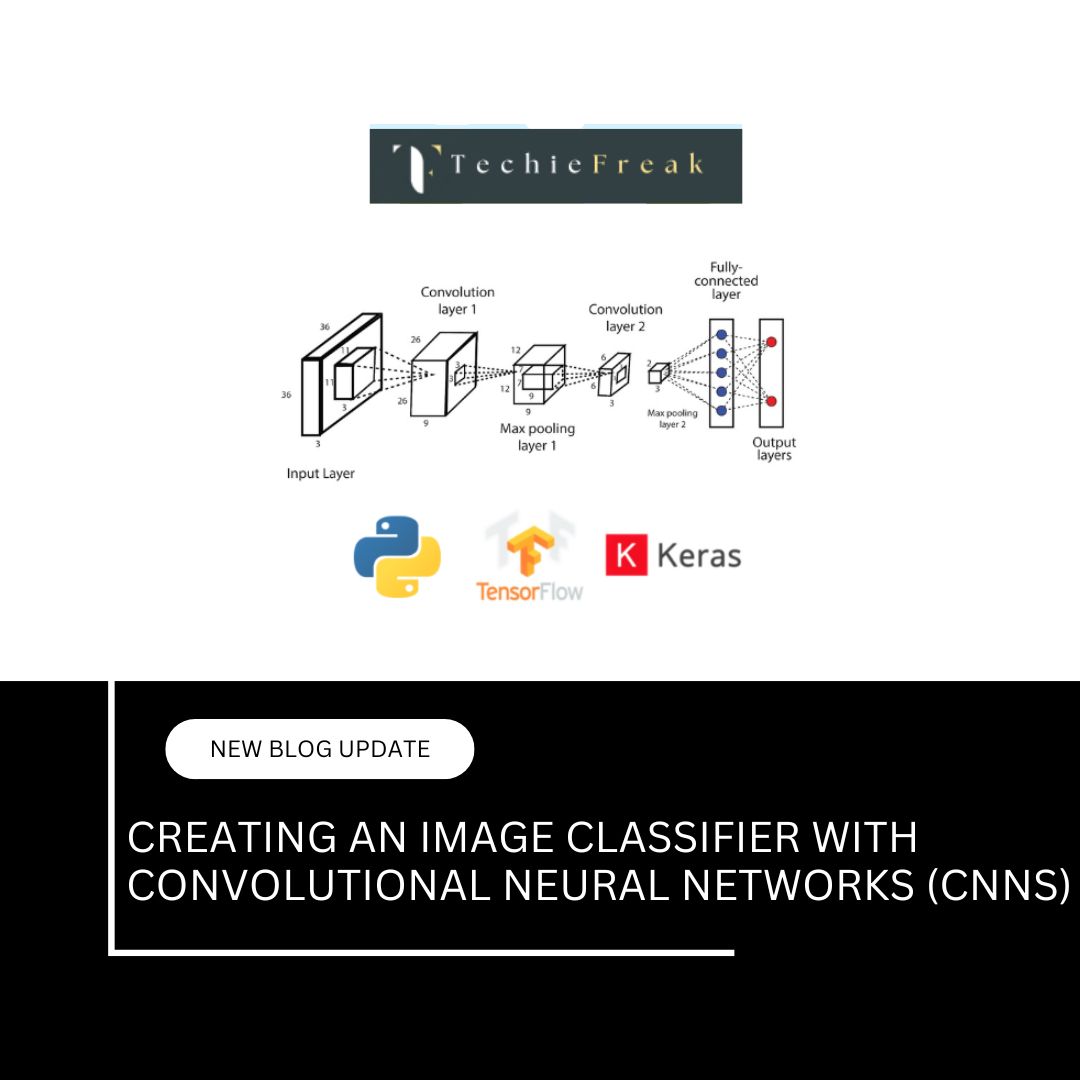
3. Computer Vision
Computer Vision allows AI to see, analyze, and interpret visual information just like humans. It processes images, videos, and real-world scenes using deep learning techniques.
How Computer Vision Works:
- Image Recognition – Identifying objects, faces, and scenes in images, such as Facebook’s face recognition.
- Object Detection – Recognizing and locating multiple objects in a frame, such as self-driving cars detecting pedestrians and traffic signs.
- Medical Image Analysis – AI analyzing X-rays and MRIs to detect diseases.
4. Expert Systems
Expert Systems are AI-driven programs designed to mimic human decision-making in specific domains using predefined rules and logic.
How Expert Systems Work:
- Knowledge Base – A database of expert knowledge, such as medical knowledge for diagnosing diseases.
- Inference Engine – Uses logical rules to analyze data and make decisions.
- User Interface – Allows humans to interact with the system, such as chatbot interfaces in customer support.
Real-World Examples of AI – Detailed Explanation
AI is deeply integrated into various industries, transforming the way we interact with technology. Here are some common applications:
1. Voice Assistants
AI-powered voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand speech, recognize commands, and provide relevant responses. They assist with tasks such as setting reminders, searching the web, and controlling smart home devices.
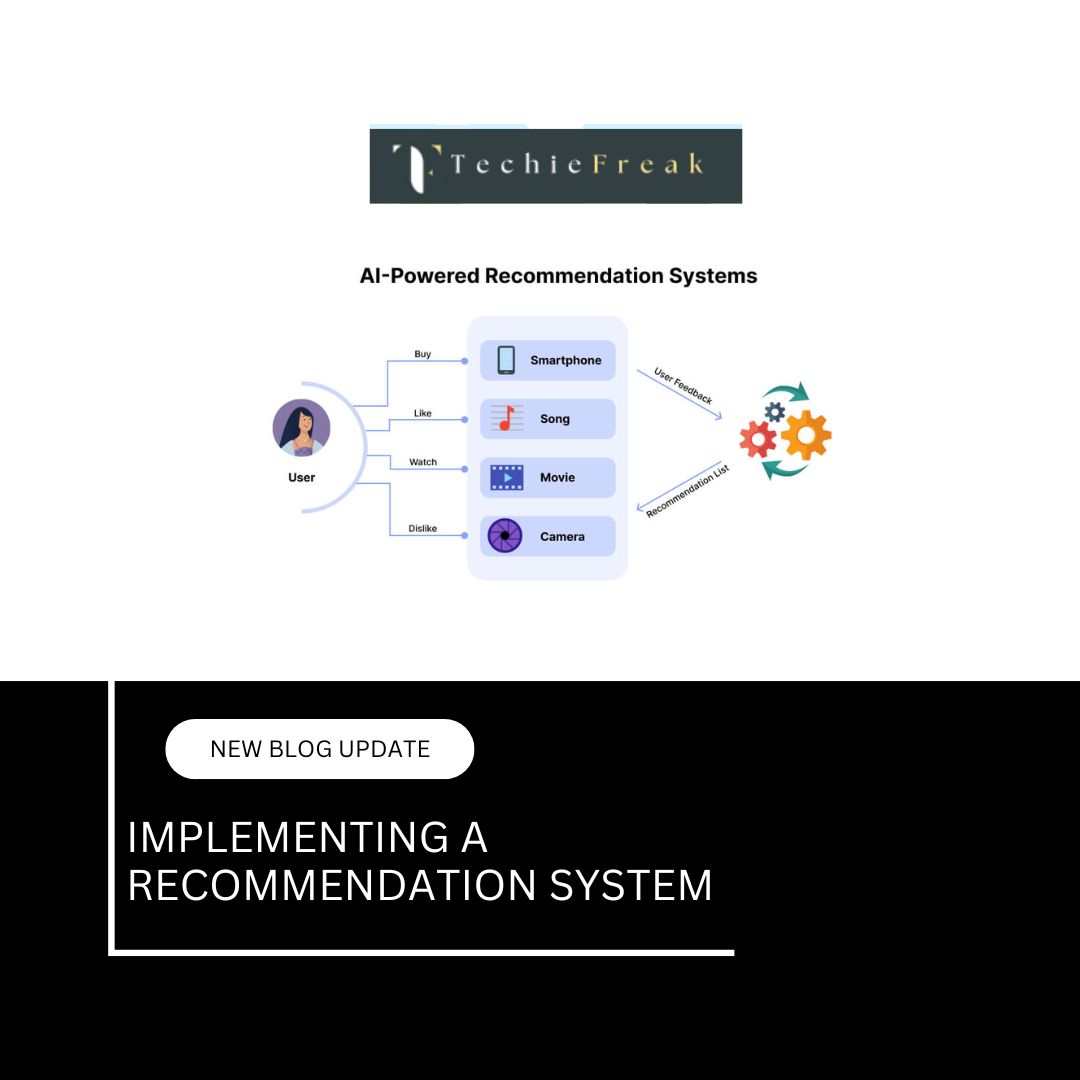
2. Recommendation Systems
Streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube, as well as e-commerce sites like Amazon, use AI to analyze user behavior and preferences. By studying past interactions, AI suggests movies, videos, or products tailored to individual interests, improving user experience and engagement.
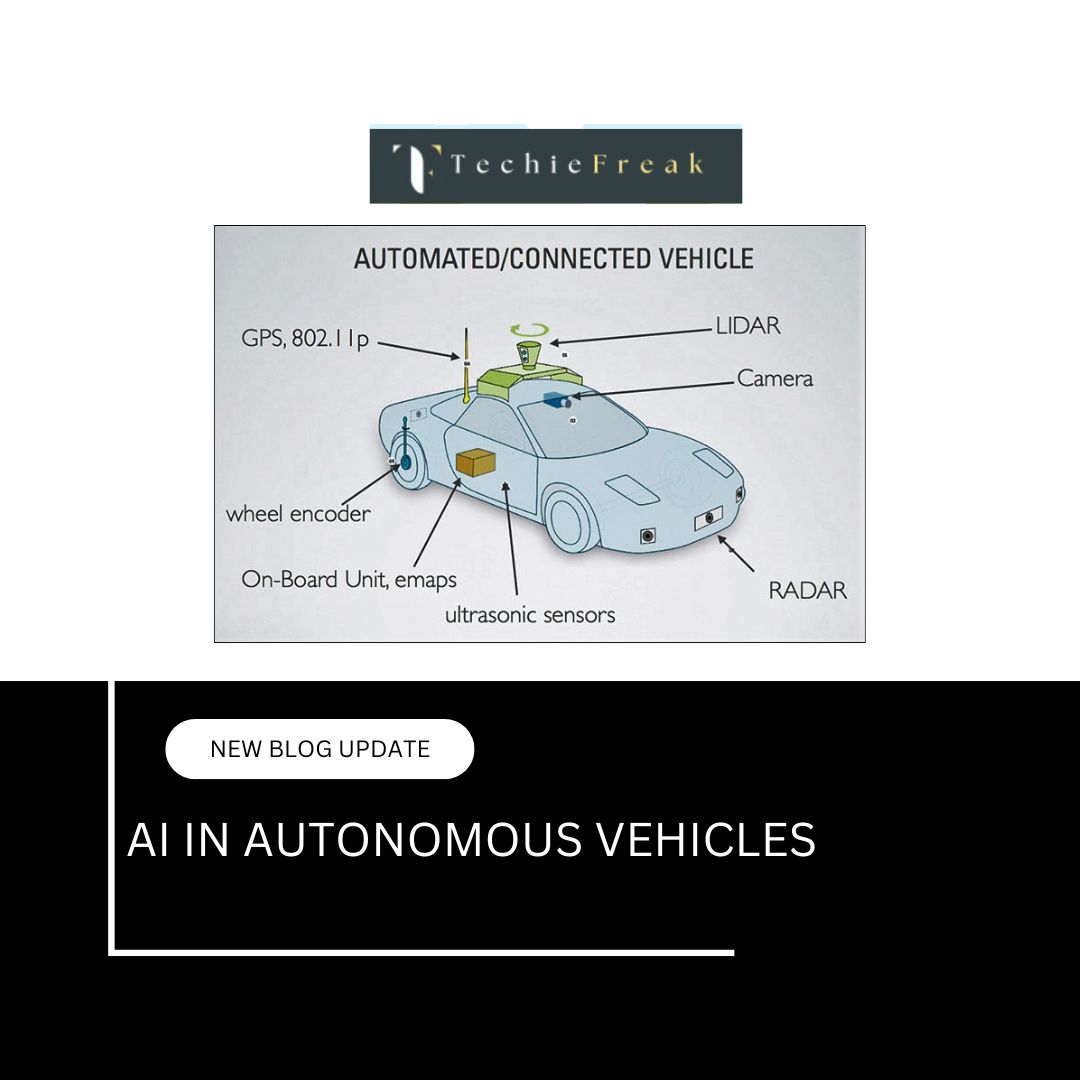
3. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars, such as those developed by Tesla and Waymo, rely on AI to interpret real-world data from cameras, sensors, and radar. AI enables vehicles to detect obstacles, recognize traffic signals, and make real-time driving decisions, reducing human intervention and increasing road safety.
4. Chatbots & Virtual Assistants
Many companies deploy AI-driven chatbots for customer support, capable of handling inquiries, resolving issues, and providing assistance 24/7. These AI systems use NLP and machine learning to understand user questions and improve over time.
5. Healthcare Applications
AI plays a crucial role in healthcare by diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images (such as X-rays and MRIs), predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. AI-powered tools like IBM Watson assist doctors in making accurate diagnoses and recommending treatments.
Key Takeaways from This Blog
- AI is already present in everyday life, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
- Voice assistants use AI to process speech and execute commands.
- AI-driven recommendation systems personalize content for users.
- Self-driving cars utilize AI for navigation and decision-making.
- AI-powered chatbots improve customer service with instant responses.
- AI is revolutionizing healthcare by aiding diagnosis and treatment planning.
Stay tuned for the next blog in our AI series, where we’ll dive into the History and Evolution of AI.
.png)



.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)