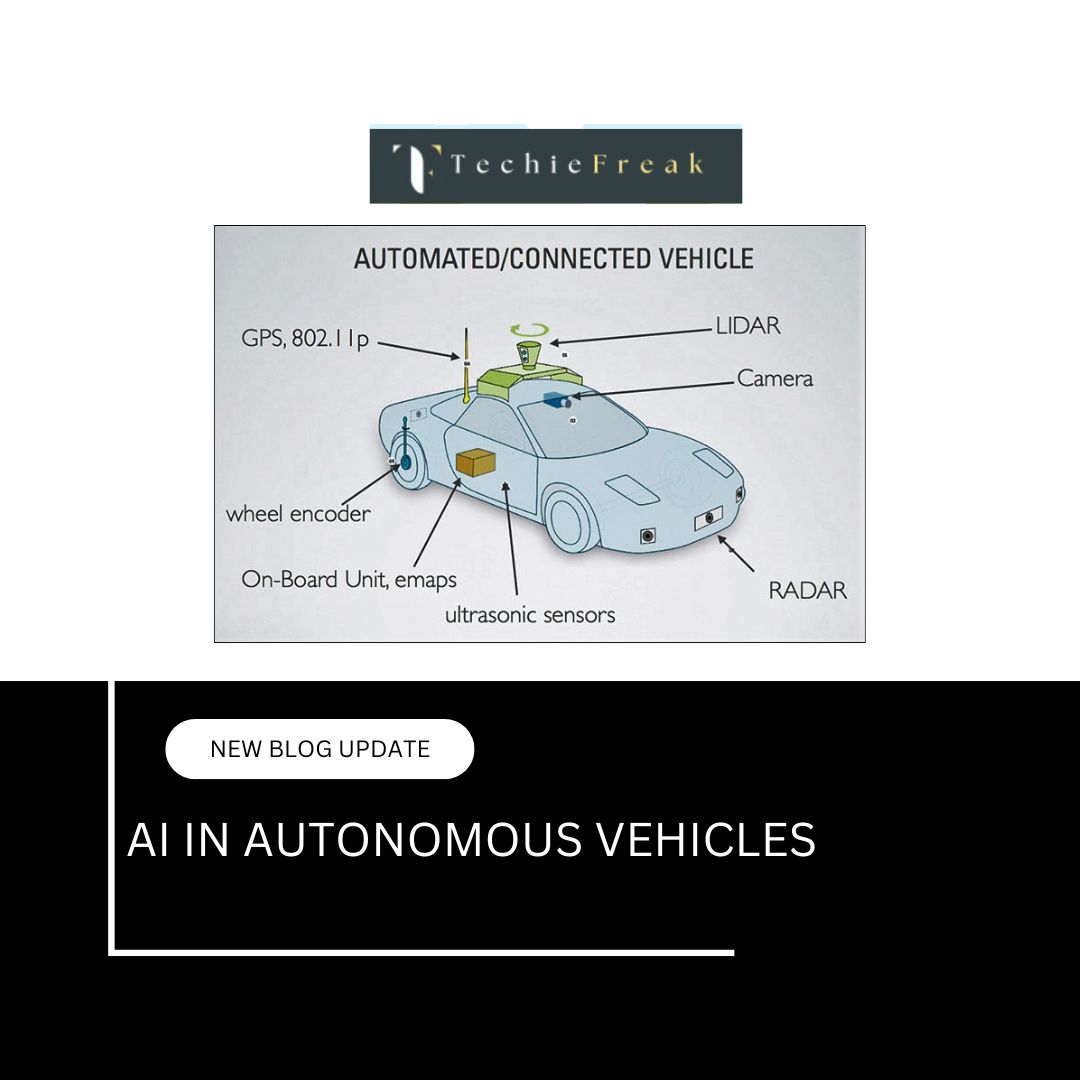
The Future of Medicine – Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Introduction
Healthcare is not just a necessity; it is a fundamental human right. However, with growing populations, aging demographics, and rising medical costs, healthcare systems globally are under immense pressure. Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI) — a revolutionary technology with the power to transform medicine from reactive to proactive, from generic to personalized, and from complex to efficient. In this blog, we dive deep into the various applications of AI in the healthcare sector and explore how it is reshaping the future of medicine.
Sure! Here's a more detailed and enriched version of both sections:
1. AI in Diagnosis and Medical Imaging
Redefining the Diagnostic Process
In traditional diagnostics, clinicians interpret medical images based on training, pattern recognition, and clinical experience. While human expertise is irreplaceable, cognitive overload, fatigue, and image complexity can lead to missed details or misinterpretation.
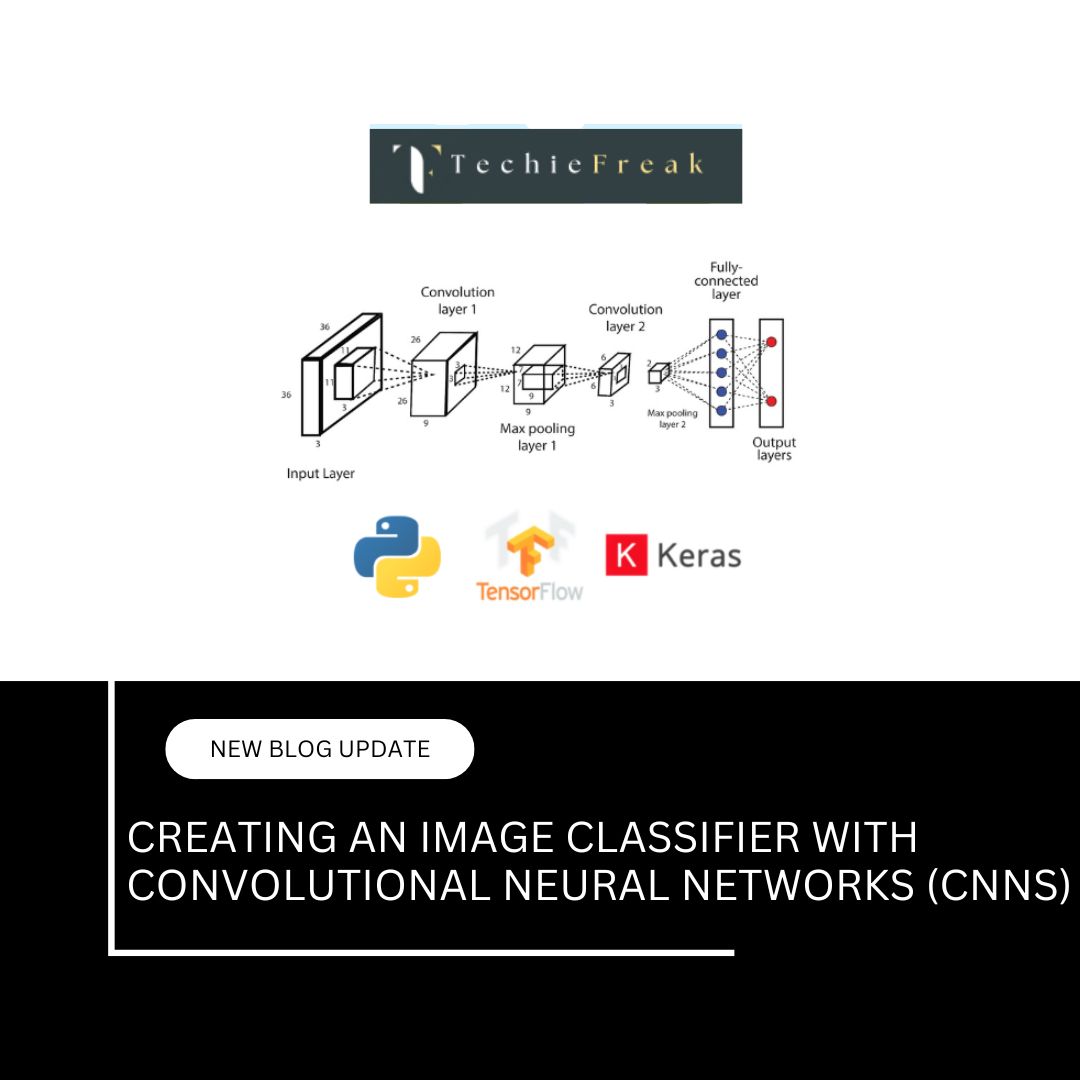
Enter Artificial Intelligence, particularly deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which are trained on millions of labeled images to identify patterns, textures, and anomalies far beyond human perception. These systems continuously improve with more data, leading to superhuman diagnostic accuracy in specific domains.
Advanced Applications
Radiology
- AI algorithms can scan imaging data (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans) and instantly flag suspicious areas.
- They detect conditions such as:
- Pulmonary nodules (potential early-stage lung cancer)
- Internal bleeding in trauma cases
- Early signs of pneumonia, TB, or COVID-19
- Tools like Aidoc and Zebra Medical Vision are being deployed in hospitals globally.
Pathology
- Digital pathology slides analyzed by AI can identify cancerous cells with higher precision and consistency than human pathologists.
- AI is also being used to grade tumors and identify molecular subtypes, which impact treatment decisions.
Ophthalmology
- Google's DeepMind built an AI tool that can detect over 50 eye diseases with accuracy matching that of top specialists, assisting in early prevention of blindness.
Dermatology
- AI apps like SkinVision and DermAssist help detect melanoma and other skin conditions using just a smartphone image.
Key Case Studies
Google Health – Breast Cancer Screening
- In a 2020 study, Google's AI model outperformed six radiologists in spotting breast cancer from mammograms.
- It reduced false positives by 5.7% and false negatives by 9.4% — crucial metrics for patient safety.
IBM Watson for Oncology
- In partnership with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, IBM Watson analyzed patient history and 300+ medical journals to recommend personalized cancer treatment options.
- Though the project has had mixed outcomes, it opened doors for integrating AI with clinical decision support.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Reduced diagnostic error rates
- Faster reporting and triaging
- Support in under-resourced settings with limited specialists
Challenges:
- Black-box decision-making: Lack of transparency in how AI reaches conclusions
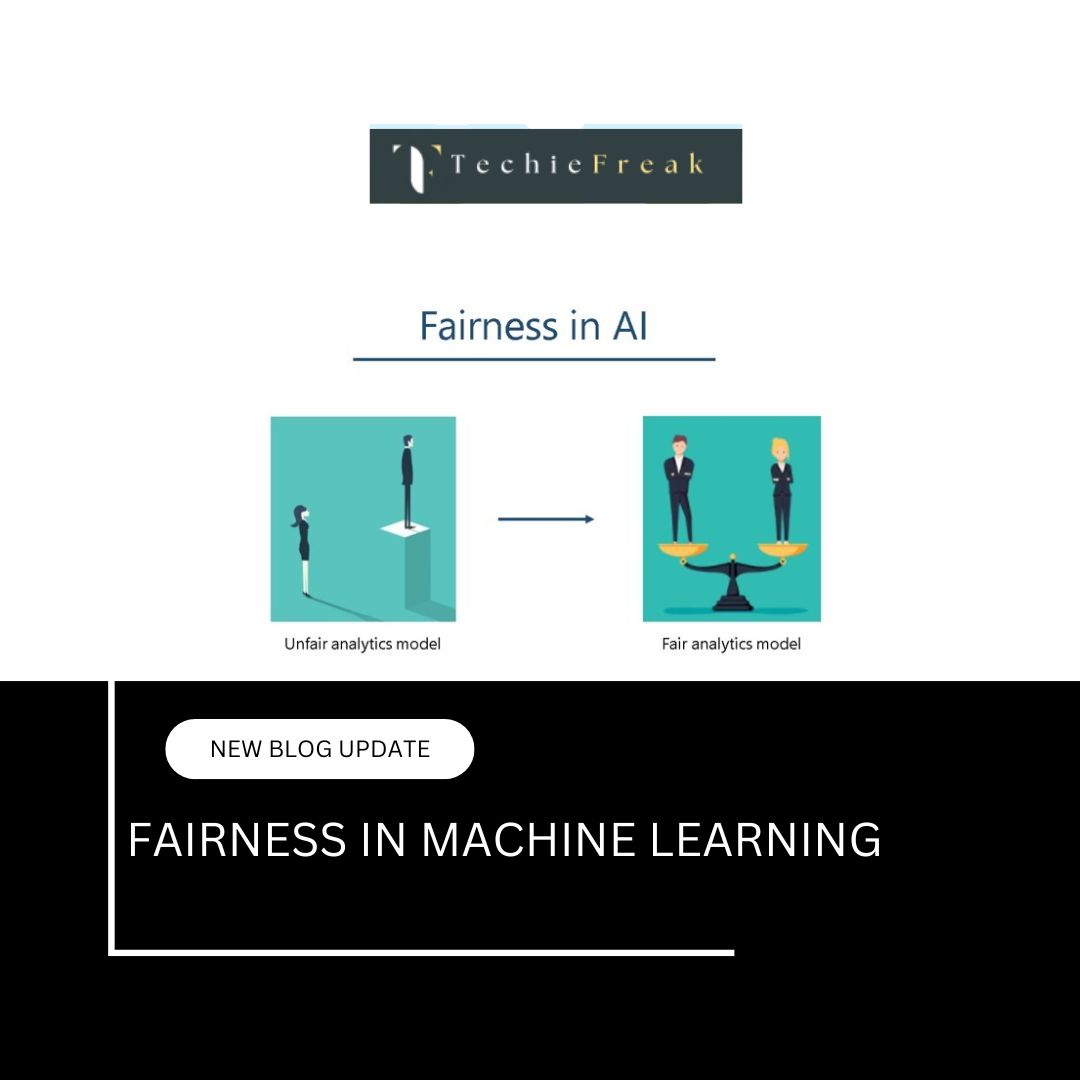
- Bias in training data: Can lead to poor performance on underrepresented groups
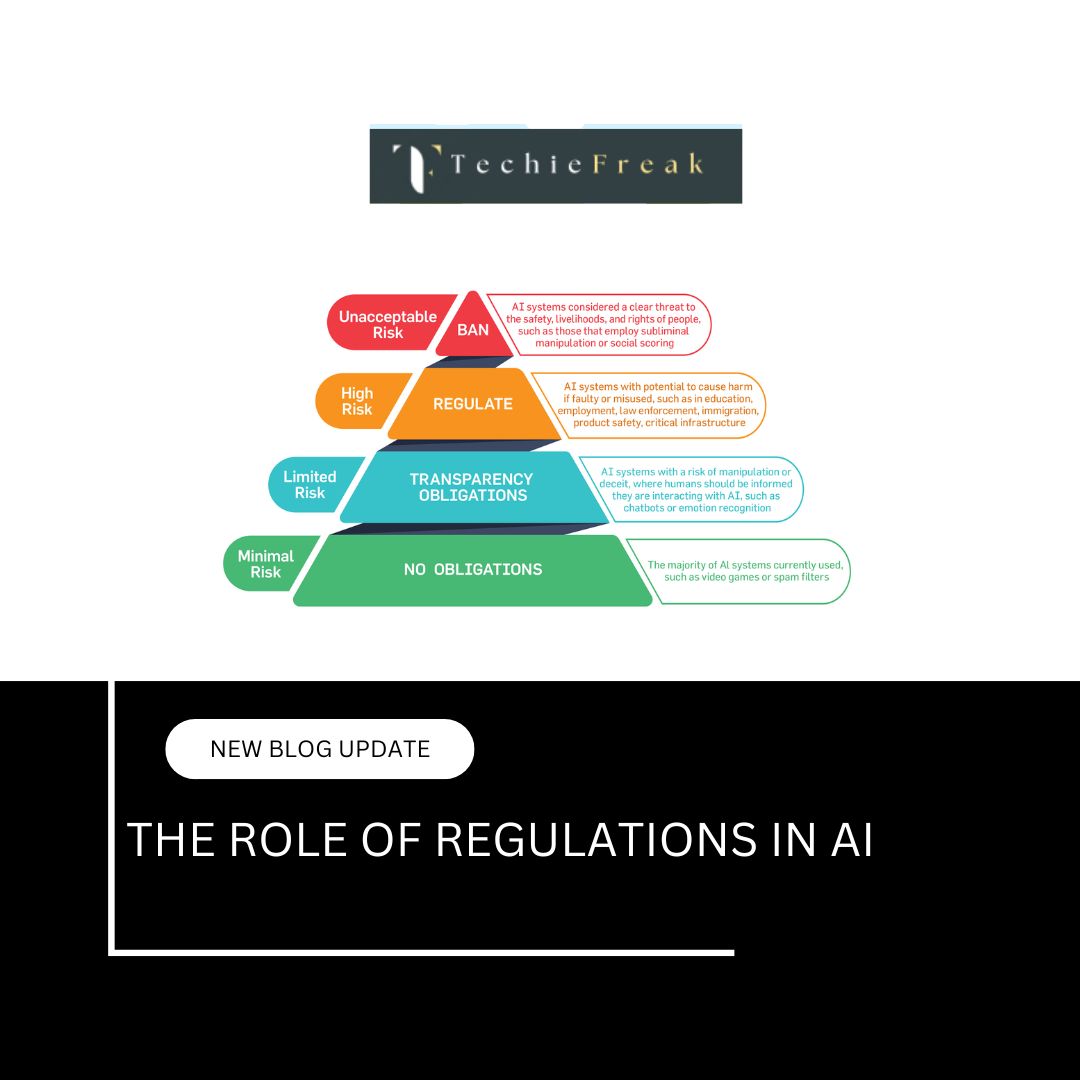
- Regulatory hurdles: Needs FDA/EMA approval for clinical use
Bottom Line: AI augments — not replaces — radiologists and pathologists. It acts as a second pair of expert eyes, catching what a human might miss and boosting diagnostic confidence.
2. Predictive Healthcare and Risk Assessment
From Treatment to Prevention
The old model of healthcare is reactive: treat the disease after symptoms appear. AI is changing that paradigm. By aggregating and analyzing large-scale data from electronic health records (EHRs), genomics, lifestyle patterns, and even wearable tech, AI can anticipate health risks before symptoms develop — enabling proactive intervention.
Applications in the Real World
Disease Outbreak Prediction
- AI algorithms can analyze travel patterns, social media, climate data, and hospital reports to predict the outbreak of infectious diseases.
- For example:
- BlueDot flagged unusual pneumonia cases in Wuhan in December 2019 — days before WHO's alert on COVID-19.
- AI-driven surveillance helped track Ebola, Zika, and Dengue spread.
Chronic Disease Risk Assessment
- AI models analyze variables like family history, BMI, lab results, sleep patterns, and more to:
- Predict onset of Type 2 diabetes
- Flag patients at risk for hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and renal failure
- Alert for mental health deterioration based on behavioral patterns
Hospital Readmission Predictions
- AI can identify patients likely to be readmitted within 30 days of discharge, allowing care teams to take preventive measures.
- This is particularly impactful in chronic disease management and post-surgical care.
Real-World Example: ForeSee Medical
- ForeSee offers predictive analytics tools used by clinicians to:
- Identify undiagnosed conditions
- Prevent unnecessary ER visits
- Stratify patients based on risk
- It integrates with EHR systems and updates insights in real-time, aiding timely intervention.
Opportunities and Ethical Dilemmas
Opportunities:
- Early intervention = better outcomes
- Reduced healthcare costs
- Personalized patient monitoring and alerts
Challenges:
- Data privacy: Who owns the prediction data?
- Over-reliance on AI: Risk of ignoring patient intuition or real-life context
- False positives: May lead to unnecessary anxiety or over-treatment
Example: Predicting that a person may develop Alzheimer's doesn’t mean they will.
Here's a more detailed and enriched version of sections 3 and 4:
3. Personalized Treatment Plans
Medicine Tailored to You
Traditional medicine often applies a “one-size-fits-all” approach — a standard treatment protocol based on population-level data. But no two patients are exactly alike. Genetics, environment, lifestyle, and even mental health can significantly affect how someone responds to treatment.
AI enables a shift to precision medicine — where treatment is customized to an individual’s unique biological and personal profile.
Key Applications of AI in Personalized Medicine
Genomic Medicine
- AI analyzes a patient's genome to identify biomarkers or mutations that affect drug metabolism or disease susceptibility.
- Helps tailor therapies, especially for complex diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and rare genetic disorders.
- Tools like Tempus and Foundation Medicine are already leveraging AI for genome-informed cancer treatment.
Real-Time Health Monitoring
- Wearables like Apple Watch, Fitbit, and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) collect heart rate, activity levels, blood oxygen, sleep data, etc.
- AI models interpret this data to:
- Detect abnormalities
- Adjust medication dosages (e.g., for insulin)
- Optimize rehabilitation or fitness plans
Behavioral and Environmental Insights
- AI considers diet, stress, location, pollution exposure, and other contextual factors to suggest personalized recommendations.
- This includes mental health interventions or early alerts about lifestyle-driven risks.
Real-World Impact
- K Health uses anonymized medical records to compare symptoms and offer treatment options tailored to each user's history.
- IBM Watson for Genomics helps oncologists match cancer patients with personalized therapies based on genomic profiling.
Benefits of Personalization via AI
- Enhanced efficacy: Right drug, right dose, right time
- Reduced side effects: Avoids trial-and-error prescriptions
- Improved adherence: Patients are more likely to follow a treatment that’s tailored to their lifestyle and biology
- Better outcomes: Especially crucial in complex diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic illnesses
AI bridges the gap between clinical guidelines and individual variability — unlocking a truly patient-centric healthcare experience.
4. Virtual Assistants and Chatbots in Patient Support
Healthcare at Your Fingertips
Imagine having a medical assistant in your pocket — answering health questions, reminding you to take medications, or even guiding you through post-op care. With AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, this is now a reality.
How They Work
These systems are trained on large medical knowledge bases (including symptom checkers, treatment protocols, and patient Q&A) and use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand user queries and respond conversationally.
Some bots use machine learning to improve accuracy over time based on patient feedback and outcomes.
Leading Platforms and Tools
Babylon Health
- Uses AI to offer chat-based consultations
- Patients input symptoms, and the AI suggests possible causes and next steps
- Integrates video calls with real doctors if needed
Ada Health
- AI-powered symptom checker available in over 140 countries
- Offers personalized health assessments and escalates urgent cases
Florence & Healthily
- Send medication reminders, track health vitals, and answer common questions
- Especially useful for patients with chronic illnesses or the elderly
Advantages of AI-Driven Virtual Healthcare
- 24/7 Availability: No appointment needed; immediate support
- Multilingual Support: Breaks down language barriers in healthcare
- Cost-Efficient: Reduces hospital visits for minor issues, saving both time and money
- Triage Capability: Directs patients to appropriate levels of care (self-care, urgent care, or emergency)
Use Cases
- Mental Health Support: Chatbots like Woebot and Wysa provide CBT-based conversations to support mental well-being.
- Post-Surgery Follow-up: Bots remind patients of wound care, medication timing, and flag complications early.
- Rural & Underserved Areas: Offers first-level care in regions lacking doctors or clinics.
🗨️ Virtual assistants are not here to replace doctors — they’re here to guide, support, and empower patients, while helping medical staff focus on complex care.
Here’s a more detailed and enriched version of sections 5 and 6 to align with the previous sections:
5. AI in Drug Discovery and Development
Accelerating Innovation in Medicine
The traditional path of drug discovery — from identifying a potential compound to final approval — can take over a decade and cost upwards of $2.6 billion. Most of this time and money is spent on failed trials or ineffective compounds.
AI is transforming this process by enabling faster, smarter, and more targeted drug development.
Key AI Technologies Revolutionizing Drug Development
Predictive Modeling
- Uses large datasets from chemical libraries and biological assays to predict the effectiveness and safety of new compounds before they reach the lab.
- Helps eliminate unlikely candidates early, saving time and resources.
Molecular Simulation & Interaction Modeling
- AI can simulate how a drug will interact with target proteins, enzymes, or receptors, drastically speeding up lead identification.
- Assesses side effects, toxicity, and metabolic pathways without relying solely on trial-and-error.
Protein Structure Prediction
- Understanding how proteins fold and function is essential for creating drugs that can bind and act precisely.
- Traditional methods took years per protein — AI now does it in minutes.
Breakthrough Example: AlphaFold by DeepMind
- Solved the “protein folding problem”, a scientific challenge that stumped researchers for 50+ years.
- Predicted 3D structures of over 200 million proteins, providing insights into how diseases progress at the molecular level.
- Accelerates vaccine development, rare disease research, and the creation of novel therapies.
Other Key Players
- Insilico Medicine: Uses AI to identify new compounds and design molecules tailored to disease-specific targets.
- BenevolentAI: Combines machine learning and drug discovery to repurpose existing drugs (notably helped identify a COVID-19 treatment candidate).
Benefits of AI in Drug Discovery
- Shorter timelines: From 10–15 years to just a few years in some cases
- Cost reduction: Cuts down R&D waste
- Higher success rates: More effective compounds enter trials
- Increased innovation: Ability to target diseases previously deemed "undruggable"
AI isn't just speeding up the process — it’s rewriting the rulebook on how we create medicine.
6. Administrative Efficiency and EHR Management
Cutting Through the Red Tape
Healthcare professionals spend an average of 35–50% of their time on paperwork, including data entry, billing codes, insurance reports, and compliance. This administrative burden not only increases stress and burnout but also reduces time spent with patients.
AI, especially NLP and automation tools, is streamlining these workflows.
Tools and Solutions Driving Efficiency
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Converts spoken or handwritten notes into structured medical records.
- Recognizes medical terminology, symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans in real-time.
- Reduces the need for manual transcription.
Smart Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems
- Uses AI to:
- Suggest relevant diagnostic codes
- Highlight missing fields
- Auto-fill forms based on previous patterns
- Flag anomalies for further review
- Some systems even offer voice-enabled inputs and chatbot-like interactions.
Real-World Example: ForeSee Medical
- Uses AI to automate the creation of comprehensive clinical documentation.
- Helps providers stay compliant while minimizing manual data entry.
- Improves record accuracy and reduces burnout.
Impact on the Healthcare Ecosystem
- Improved patient experience: Doctors are more present and less distracted by screens.
- Faster recordkeeping: Supports continuity of care and better handoffs between specialists.
- Better data quality: AI reduces human errors in documentation and helps generate useful analytics.
AI takes on the paperwork so that doctors can get back to what matters most — healing people.
Would you like me to complete the final parts on robotic surgeries, AI in mental health, or a summary of future trends?
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is not a distant dream for the healthcare industry — it is a present-day reality. From diagnosing life-threatening diseases to tailoring treatments and improving operational efficiency, AI is revolutionizing every corner of the medical world.
While challenges such as data privacy, regulatory compliance, and algorithmic bias still exist, the benefits of AI in healthcare are undeniable. With continued innovation and responsible implementation, the future of medicine is not just brighter — it’s smarter.
AI is making healthcare more accessible, more efficient, and more human-centered. The next chapter of medicine is already being written — by machines and humans, together.




.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)