Part 1- Tools for Text-Based AI: ChatGPT
1. Introduction to ChatGPT
1.1 What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a conversational AI model developed by OpenAI. It is based on the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) architecture, which is designed to generate human-like responses in a dialogue format. ChatGPT can understand user inputs (prompts), maintain context across a conversation, and generate informative, creative, and contextually appropriate responses.
1.2 Evolution of ChatGPT
- GPT-1 (2018): First proof of concept using 117M parameters.
- GPT-2 (2019): Demonstrated coherent text generation with 1.5B parameters.
- GPT-3 (2020): Significantly improved with 175B parameters.
- ChatGPT (2022): Fine-tuned version of GPT-3.5 with dialogue capabilities.
- GPT-4 (2023): Multimodal input support and better reasoning skills.
1.3 Real-world Applications
- Virtual assistants (e.g., Alexa, Siri-like apps)
- Chatbots for customer service
- Coding assistants (e.g., GitHub Copilot)
- Content generation (blogs, emails, reports)
- Language translation
2. How ChatGPT Works Internally
2.1 The Transformer Architecture
ChatGPT is built on the Transformer architecture, a deep learning model introduced in the 2017 research paper “Attention is All You Need”. The Transformer has revolutionized natural language processing (NLP) by enabling models to understand context and long-range dependencies better than traditional models like RNNs or LSTMs.
While the original Transformer has two components—an encoder and a decoder—ChatGPT uses only the decoder part of the architecture. This is because ChatGPT is designed for language generation, not for translation or other sequence-to-sequence tasks that require both encoding and decoding.
Let’s break down the key components of the Transformer architecture used in ChatGPT:
Self-Attention Mechanism
This mechanism allows the model to consider other words in the input when processing each word. For instance, when predicting the next word in the sentence "The animal didn’t cross the road because it was tired", the model needs to determine whether "it" refers to "animal" or "road". The self-attention mechanism assigns weights to different parts of the input so that the model can focus on the relevant word ("animal" in this case).
Feedforward Neural Networks
After the self-attention layer, the model passes the output through a feedforward network—a series of fully connected layers. These layers help the model learn complex patterns by transforming the attention outputs into deeper representations of the input text.
Positional Encoding
Unlike RNNs, Transformers process all words in a sentence at once and thus do not inherently understand the order of words. To address this, positional encodings are added to the token embeddings. These encodings inject information about the position of each word in the sequence, allowing the model to differentiate between sentences like "John loves Mary" and "Mary loves John".
2.2 Pre-training Phase
In the pre-training phase, the model learns the basic structure and meaning of human language by reading a vast amount of publicly available text from books, websites, forums, and articles.
Objective: Next-Token Prediction
The goal during pre-training is to predict the next word (technically, the next token) in a sentence. For example, given the input:
"The sky is",
the model should predict: "blue".
The model learns by minimizing the difference between its predicted output and the actual word that follows in the training data. This is done using a loss function (typically cross-entropy loss) and backpropagation.
Nature of Learning: Unsupervised
This phase is considered unsupervised because the model does not require labeled data. It simply learns from raw text, inferring rules and patterns from the structure and co-occurrence of words.
2.3 Fine-tuning Phase
Once pre-training is complete, the model undergoes fine-tuning to align it better with specific use cases—such as answering questions or having helpful and polite conversations.
Supervised Fine-Tuning
Human AI trainers generate example conversations where they simulate both the user and the assistant. These examples are used to guide the model to produce desirable responses. This stage ensures the model understands how to behave like a helpful conversational agent.
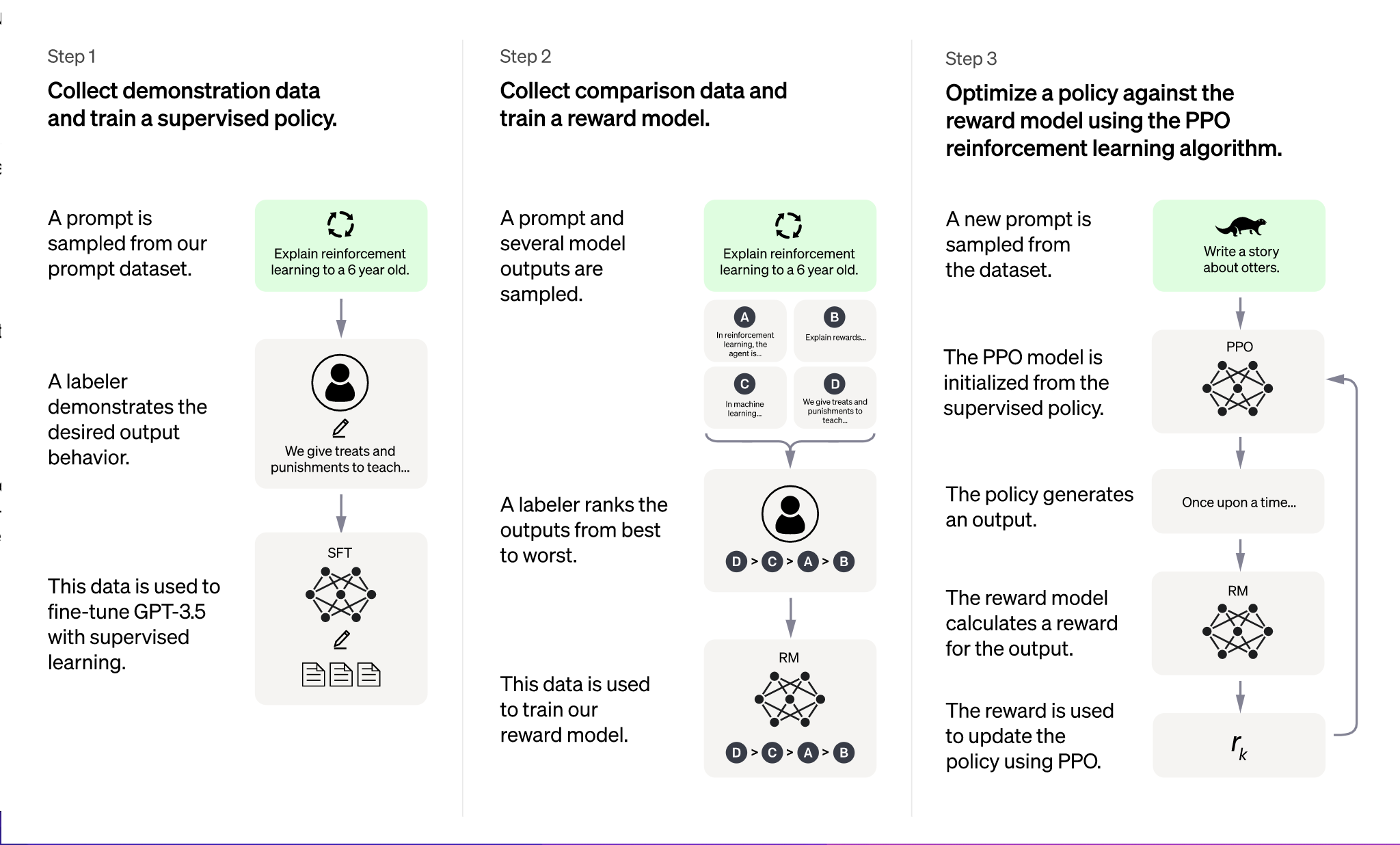
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
Fine-tuning also includes a more advanced stage called Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). This process involves several steps:
- The model generates multiple possible responses to a given user prompt.
- Human reviewers rank these responses from most to least appropriate based on relevance, safety, and helpfulness.
- A reward model is trained using these rankings to score future responses.
- The model is then optimized using a reinforcement learning algorithm called Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), which encourages it to generate higher-scoring responses.
This process helps the model produce responses that are not only contextually correct but also align with human values and safety guidelines.
2.4 Tokenization
Before any input text can be processed by ChatGPT, it must be converted into a numerical format the model can understand. This process is known as tokenization.
What is a Token?
A token is a basic unit of text. Depending on the tokenizer, a token may represent:
- A single word (e.g., "apple")
- A sub-word or word piece (e.g., "un-", "break", "-able")
- A punctuation mark or space
Byte Pair Encoding (BPE)
ChatGPT uses a method called Byte Pair Encoding (BPE). BPE begins with individual characters and iteratively merges the most frequent pairs of characters or character sequences into longer tokens. This allows the tokenizer to balance between having a compact vocabulary and being able to handle out-of-vocabulary or rare words.
Example
Let’s take the word: "ChatGPT"
Using BPE, it might be split into tokens like:
- "Chat"
- "G"
- "PT"
Similarly, a sentence like "ChatGPT is amazing!" might be tokenized as:
- "Chat"
- "G"
- "PT"
- " is"
- " amazing"
- "!"
Why Tokenization Matters
Tokenization affects:
- Input size: The model can only handle a fixed number of tokens (e.g., GPT-4 can handle up to 32,000 tokens).
- Accuracy: The choice of tokenizer can influence how well the model understands and generates text.
- Speed and memory usage: More tokens mean more computation, so efficient tokenization is important for performance.
3. Step-by-Step Internal Workflow of ChatGPT
Understanding how ChatGPT processes an input and generates an output requires examining its internal workflow—from the moment a user enters a prompt to the point where a complete response is returned. This chapter breaks down the entire process into five main phases, each responsible for specific tasks in the language generation pipeline.
3.1 User Input Phase
The process begins when a user types a message, such as:
Example Input:
“Explain quantum computing in simple terms.”
Step 1: Tokenization
Before the model can process the text, it must convert the input string into a format it understands. This involves breaking the sentence into tokens—subword units derived using Byte Pair Encoding (BPE).
For instance:
"Explain quantum computing in simple terms."
May become:
["Explain", " quantum", " computing", " in", " simple", " terms", "."]
Step 2: Numerical Encoding
Each token is then mapped to a unique token ID, which is an integer representation from the model’s vocabulary.
Example:
"Explain" → 15496
"quantum" → 10843
and so on...
The result is an array of numbers that the model can process:
[15496, 10843, 14672, 287, 12455, 1089, 13]
3.2 Context Management
ChatGPT is designed to handle multi-turn conversations. To maintain continuity and coherence, the system keeps track of previous exchanges using a message history format that separates inputs based on roles:
- system: Provides instructions on the assistant's behavior
- user: Contains prompts from the user
- assistant: Contains model responses
Example Message History:
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is quantum computing?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Quantum computing is a type of computation..."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Explain it in simple terms."}
]
This format enables context awareness, allowing the model to tailor responses based on prior interactions, ensuring it doesn't "forget" the conversation’s flow.
3.3 Inference Phase (Forward Pass)
Once the input is tokenized and contextualized, it moves to the model inference phase—where predictions are made.
Step 1: Passing Through Layers
The tokenized input is fed through multiple transformer layers. Each layer consists of:
- Self-Attention Sub-layer: Assigns weights to different parts of the input to understand relationships and focus areas.
- Feedforward Network: Processes the attention outputs and refines the understanding of context.
- Residual Connections & Layer Normalization: Enhance training stability and performance.
Step 2: Attention Mechanism
The self-attention module calculates how much each word should pay attention to every other word in the input.
For example, when the model sees:
"Explain quantum computing in simple terms."
It might pay higher attention weights to "quantum" and "simple" when generating the response.
Step 3: Output Probability Distribution
At the output of the final layer, the model computes a probability distribution over its entire vocabulary (which includes tens of thousands of tokens).
It predicts:
“Given the input sequence, what is the most likely next token?”
This is computed using a softmax function, which converts raw scores (logits) into probabilities.
3.4 Output Generation
Step 1: Token Sampling
The model selects the next token based on the output probability distribution. There are several strategies for doing this:
- Greedy decoding: Choose the highest probability token.
- Temperature sampling: Introduce randomness (higher temperature = more creative outputs).
- Top-k / Top-p sampling: Limit choices to top-k most probable tokens or until cumulative probability exceeds p.
Step 2: Iterative Generation
The selected token is appended to the input sequence, and the updated sequence is fed back into the model. This loop continues until:
- An end-of-sequence token is generated (e.g., ``), or
- A predefined token limit is reached (e.g., 2048 tokens in GPT-3.5 or 32,000 tokens in GPT-4).
Step 3: Decoding
Once the model completes token generation, the final list of token IDs is converted back to human-readable text using the tokenizer's decode function.
3.5 Example: End-to-End Generation
Let’s walk through a complete example:
User Input:
“Write a poem about the moon.”
Internal Workflow:
- Tokenization
- Input is split: ["Write", " a", " poem", " about", " the", " moon", "."]
- Token IDs: [8785, 257, 1332, 1212, 262, 7645, 13]
- Context Management
- Conversation state is updated with this user prompt.
- Model reads previous dialogue if available.
- Forward Pass
- Tokens pass through transformer layers.
- Attention maps are calculated.
- The model identifies thematic context from words like "poem" and "moon".
- Token Generation
- Model outputs tokens like:
[The, moon, shines, bright, on, a, winter, night, ...] - Sampling continues until the sequence is complete.
- Model outputs tokens like:
- Decoding
Tokens are mapped back to text:
“The moon shines bright on a winter night…”
This end-to-end process usually takes just a few milliseconds on optimized hardware during deployment.
Summary of the Workflow
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| User Input Phase | Tokenizes and encodes input text into numerical format |
| Context Management | Maintains multi-turn dialogue history with role-based message encoding |
| Inference Phase | Processes input through transformer layers to compute token probabilities |
| Output Generation | Iteratively samples next tokens and decodes them into human-readable output |
| Example | Demonstrates the full workflow from input to poem generation |




.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)