Revolutionizing Entertainment – AI in Gaming and Entertainment
Introduction
The world of gaming and entertainment has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years—and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is at the heart of this change. From smarter NPCs (non-player characters) in games to personalized movie recommendations, AI is reshaping how we play, watch, and experience content. It’s not just about better graphics or sound anymore—AI is crafting dynamic, immersive experiences tailored to individual preferences.
In this blog, we’ll explore how AI is revolutionizing the gaming and entertainment industries—across development, gameplay, audience engagement, content creation, and more.
Here's a detailed and expanded version of sections 1 and 2 for your blog on "AI in the Gaming Industry", enriched with deeper insights and technical context—while keeping it engaging and informative:
1. Smarter Gaming: AI in Game Development and Gameplay
AI has revolutionized the gaming experience by making in-game environments more immersive, responsive, and lifelike. From enemy behavior to world-building, AI adds a new level of depth and personalization that traditional programming cannot achieve.
Adaptive AI for Smarter Gameplay
Modern games leverage adaptive artificial intelligence to make non-playable characters (NPCs) smarter and more human-like. Unlike scripted behaviors that repeat predictably, AI-powered NPCs can:
- Learn from player actions and adjust their strategies over time. For example, if a player always uses stealth tactics, AI enemies may begin to scan for hidden threats more frequently.
- React contextually to changing in-game environments, weather, or the player's health and resource status.
- Collaborate or compete in complex ways, offering richer gameplay and emotional stakes.
This creates gameplay that feels unique for each player, increasing replay value and engagement.
Procedural Content Generation (PCG)
AI is also being used to design game environments and missions without manual input from developers. This is called procedural content generation, and it allows for virtually infinite possibilities within a game world.
- Minecraft and No Man’s Sky are standout examples, where vast landscapes, biomes, and quests are created algorithmically.
- AI ensures that each generated world is not only different but also balanced and playable—a major leap from earlier randomized systems.
Case Study: Middle-Earth – Shadow of Mordor
This game introduced the groundbreaking Nemesis System, which uses AI to create dynamic relationships between the player and enemies:
- Enemies remember past battles, taunt the player differently based on previous encounters, and even rise in rank after defeating the player.
- This system personalizes the storyline, making each playthrough unique and emotionally engaging.
2. AI in Game Testing and Quality Assurance
Behind every successful game lies thousands of hours of testing. AI is transforming this traditionally manual and repetitive process into a faster, more reliable, and intelligent phase of development.
How AI Automates Game Testing
Rather than relying solely on human testers, studios now use AI-powered bots to:
- Simulate thousands of hours of gameplay in minutes—testing every path, action, and scenario imaginable.
- Identify bugs, glitches, and balance issues that might go unnoticed during human testing.
- Stress test mechanics, such as collision detection, item interactions, and multiplayer sync.
These bots are trained using reinforcement learning, allowing them to adapt and explore as a player would, but with far more speed and consistency.
Machine Learning in Quality Control
AI models can be trained on historical data to predict where bugs are most likely to appear based on code changes, game mechanics, or prior version issues. This leads to:
- Faster bug detection
- Smarter prioritization of issues
- Cost-effective testing cycles
Example: EA Sports and FIFA Series
EA Sports uses AI to test its popular FIFA series. With AI:
- Every kick, pass, and tackle is simulated under different scenarios to maintain fluidity and realism.
- The AI ensures that player stats, game physics, and scoring mechanics remain balanced across updates and difficulty levels.
Here’s a more detailed and expanded version of sections 3 and 4 for your "AI in the Gaming Industry" blog, adding more technical insights and examples:
3. Personalization and Player Experience
In the age of tailored entertainment, AI is making a significant impact on the personalization of gaming experiences. By analyzing player behavior and preferences, AI not only adjusts gameplay elements but also enhances user engagement and satisfaction.
How AI Personalizes Player Experiences
AI systems track players’ in-game actions, choices, and habits, using this data to customize and evolve the gaming experience in real-time. Here’s how it works:
- Mission and Quest Recommendations: AI analyzes your past choices, playstyle, and interests to suggest missions or quests that align with your preferred game modes. For example, if you enjoy stealth gameplay, the system may highlight missions involving covert operations.
- Weapons and Character Upgrades: Based on gameplay behavior (e.g., your tendency to use ranged weapons over melee), AI will recommend specific upgrades or character builds that fit your style. It also helps players avoid overwhelm by providing targeted suggestions.
- Real-Time Difficulty Adjustment: AI can dynamically adjust the game difficulty based on the player’s skill level. If a player is struggling, the AI can decrease the difficulty subtly (e.g., by adding more health packs or slowing down enemy reactions). On the other hand, if the player is breezing through, the AI can ramp up challenges to keep the game engaging.
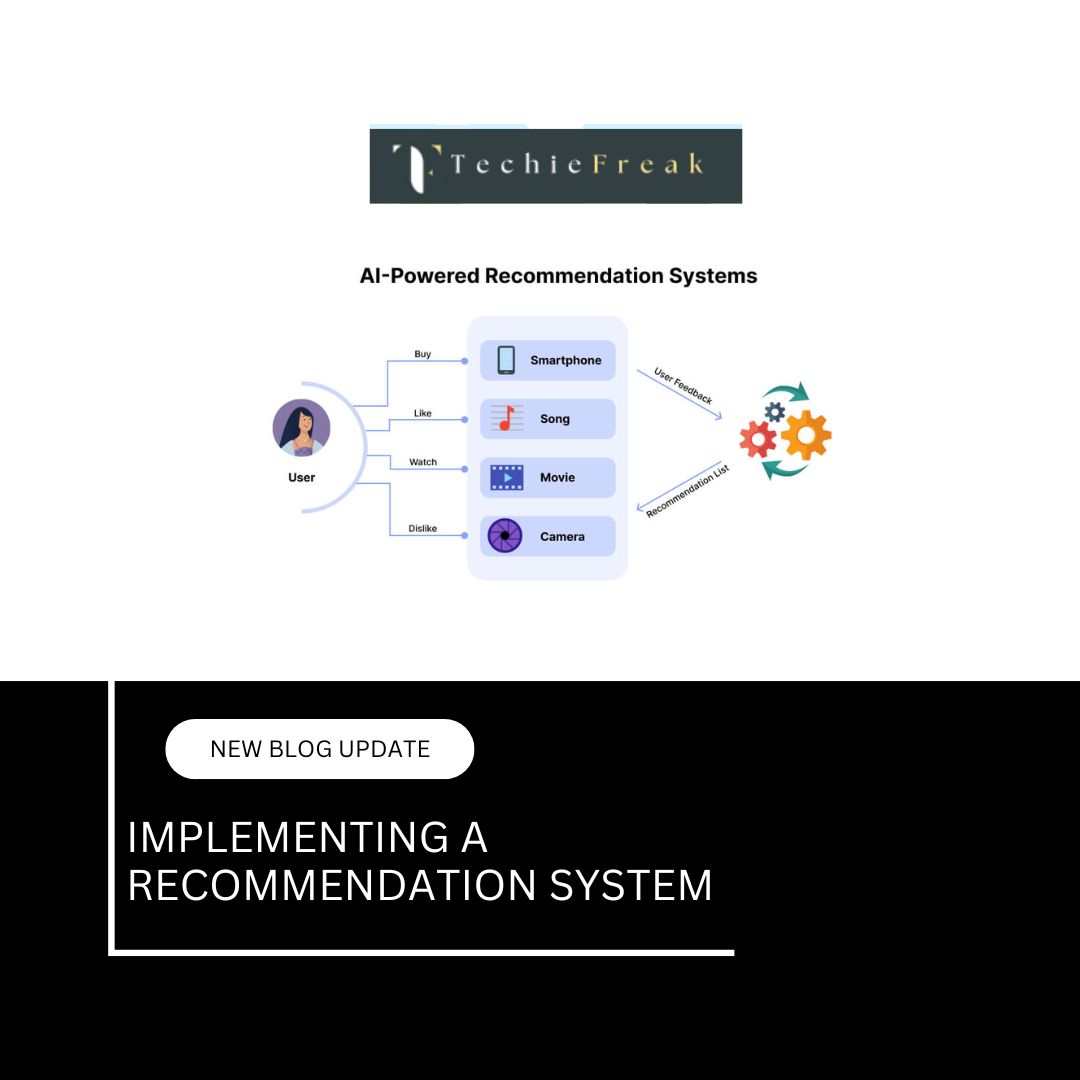
Recommendation Engines in Gaming Platforms
Just like AI-driven systems on Netflix or Spotify, platforms like Steam and Xbox Game Pass are using AI to recommend games to players based on their preferences, playstyle, and past purchases. These platforms use recommendation algorithms that:
- Consider your play history (genres, types of games played, completion rates).
- Factor in the social aspect, showing games your friends have enjoyed or games with similar trends.
- Suggest content with similar ratings and themes, ensuring you're never short of fresh content that matches your taste.
These recommendation engines help users discover hidden gems they might not have found otherwise, fostering a more personalized and engaging gaming experience.
4. AI in Animation and Visual Effects (VFX)
In addition to gameplay mechanics, AI is making waves in animation and visual effects (VFX), areas traditionally known for their high costs and long production times. AI is transforming how animation studios and filmmakers work, offering powerful tools that enhance creativity, reduce manual labor, and speed up production.
AI Tools Revolutionizing Animation and VFX
AI is being integrated into several aspects of animation and VFX production:
- Facial Recognition and Expression Synthesis: AI-driven systems like DeepFaceLab are used to capture and enhance facial expressions. AI algorithms analyze facial muscles and expressions in real-time, improving the realism of animated characters or actors in VFX scenes. This is especially beneficial for creating hyper-realistic animated characters or deepfake technology where emotions can be convincingly portrayed.
- AI-Generated Backgrounds: AI algorithms are increasingly used to create virtual landscapes or dynamic backgrounds. Games or films that require massive, changing environments (e.g., cities or forests) can rely on AI to generate environments that are not only visually stunning but also adaptively interactive.
- Crowd Simulations: AI can simulate large crowds with realistic behavior, responding to environmental stimuli or directing their attention to certain events. This is particularly useful in creating high-density scenes like battlefields, stadiums, or public gatherings in games and films.
- Motion Capture Enhancements: AI can refine and enhance motion capture data, smoothing out unnatural movements or improving the accuracy of physical gestures. It even allows animators to modify character movements in post-production without needing additional sessions.
Real-World Examples
- Disney and Pixar have been using AI-assisted tools for years to create emotionally nuanced animations. These tools help in automating facial animation, making characters' emotional expressions more believable and fluid, enhancing viewer immersion.
- Deepfake Technology is being explored not only for voice dubbing but also for reanimating characters, making older actors look younger or allowing voices from one actor to be mapped onto another’s face. This is a game-changer for animation and film production, opening up new creative possibilities while reducing costs.
Here’s a detailed and expanded version of sections 5 and 6:
5. AI-Powered Content Recommendation Systems
AI has seamlessly integrated into our digital lives, shaping the content we consume daily, often without us even realizing it. Content recommendation systems powered by AI influence platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube, making suggestions that feel almost tailored to perfection.
How Recommendation Engines Work
At the core of these platforms lies a set of algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data to predict and suggest content. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Behavioral Data: AI systems track your interactions with content—such as what you watch, listen to, or click on—to build a profile of your tastes and preferences. This includes analyzing:
- Watch history: The genres, themes, or types of content you've previously engaged with.
- Interaction patterns: How long you spend on specific content, your re-watch habits, and what keeps you engaged.
- Device Type and Time of Day: AI adapts suggestions based on whether you're watching on a mobile, desktop, or smart TV, and when you typically use the platform (e.g., during commute times, late at night).
- Advanced Algorithms:
- Collaborative Filtering: This method analyzes data from multiple users and makes recommendations based on shared interests. If other users who watched the same movies as you also enjoyed a certain show, it’ll likely recommend that show to you.
- Deep Learning: AI models use deep neural networks to understand subtle patterns in the data, even identifying content you might not know you’d like based on your interaction history.
Platforms Using AI
- Netflix: Netflix uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze your watching patterns and user ratings to suggest new shows and movies. It also takes into account factors like genre preferences and even the time of day you watch content to tailor recommendations further.
- Spotify: By analyzing listening habits and audio characteristics, Spotify’s AI-driven playlist curation tools like Discover Weekly and Release Radar offer personalized music playlists. AI also adapts to your changing musical preferences, constantly improving the recommendations.
- YouTube: YouTube's recommendation engine uses data like watch time, likes, comments, and subscriptions to suggest videos. It also considers content types that keep you engaged and suggests similar creators or topics based on your interactions.
These AI-powered recommendation engines are key to creating an engaging, personalized experience, ensuring users always find something they’ll love.
6. AI in Music and Art Creation
AI is revolutionizing creative fields, empowering artists and musicians to collaborate with machines in ways that were previously unimaginable. Whether in music composition, visual arts, or video editing, AI has become a co-creator, generating original works and transforming traditional creative processes.
AI in Music Composition
AI is now capable of composing background scores, theme music, and even entire albums, making music production more efficient and accessible. Here’s how it’s being used:
- Tools for Music Composition:
- AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist): AIVA is an AI music composer that can generate original compositions in various genres, from classical to contemporary. It analyzes existing music to understand style, rhythm, and melody to create original pieces.
- Amper Music: A tool that enables users to create customized music tracks by specifying mood, style, and tempo. Amper uses AI to adjust and produce music that fits the specific needs of the user.
- OpenAI’s MuseNet: A deep neural network that can generate full-length music compositions across various genres and in the style of renowned composers or modern artists. MuseNet creates high-quality music using deep learning techniques, offering creative possibilities that were once only available to skilled musicians.
These tools are not only reducing production costs but also democratizing music creation, enabling anyone—regardless of their musical training—to experiment and create high-quality compositions.
AI in Visual Arts
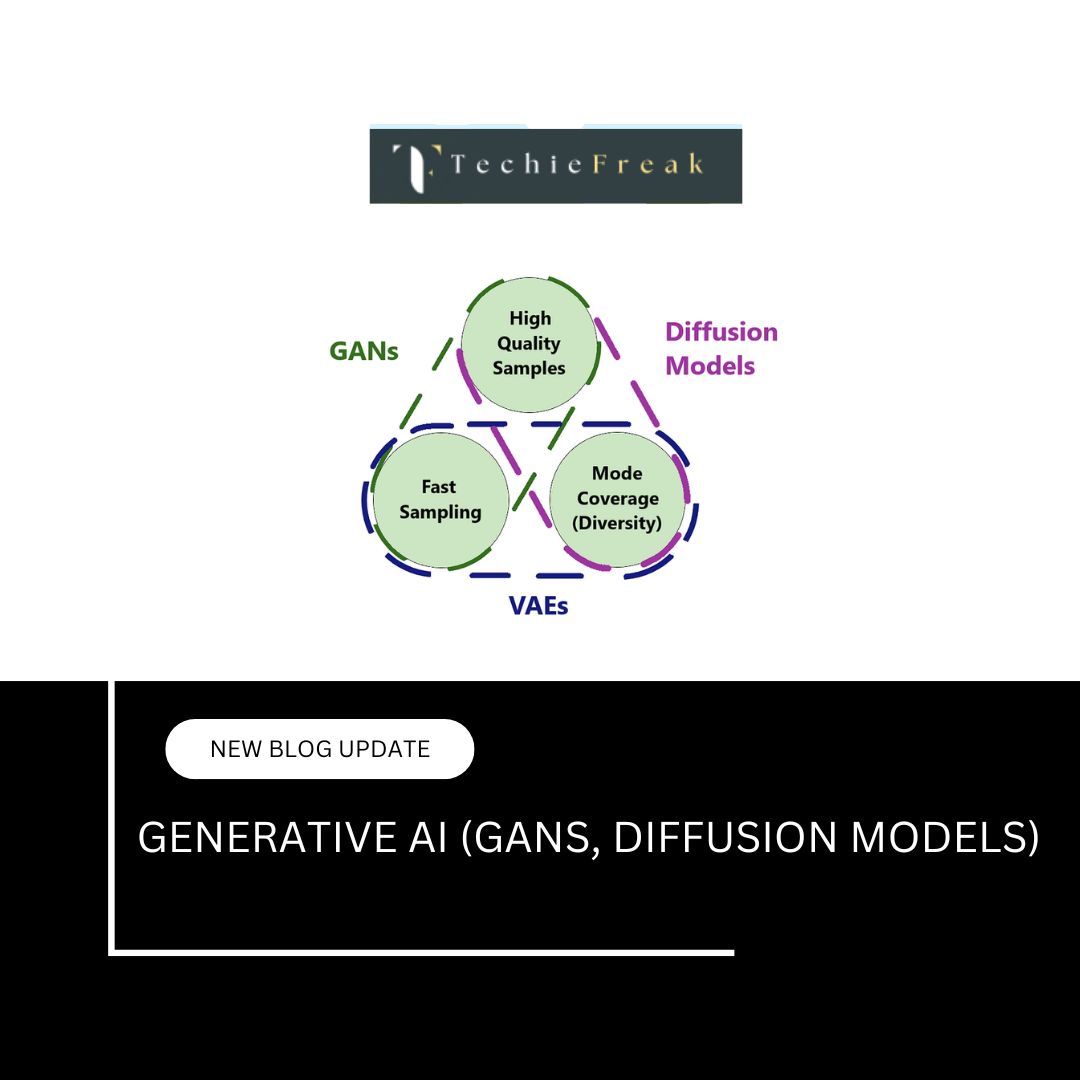
In the world of visual arts, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are at the forefront of AI-driven creativity. GANs allow machines to generate new visual art by learning from existing artwork and creating unique pieces based on that learning.
- GANs in Art Creation:
- Character Design: AI can help in creating original character designs, concept art, and visual storyboards, enabling artists to experiment with unique styles and features.
- Artwork Generation: AI tools like DeepArt and Artbreeder use GANs to create digital artwork that blends elements of different artistic styles. These tools generate one-of-a-kind pieces that are used in game design, movie production, and even NFT creation.
- AI in Video Editing:
- AI has also found a place in video editing, where it assists with color grading, editing, and transition effects. For example, AI can automatically apply color correction based on the mood of a scene, or it can smooth transitions between shots, saving time and effort for editors.
Impact on Creativity and Production
AI’s involvement in art and music creation has several key impacts:
- Reduced Production Costs: By automating parts of the creation process, AI cuts down on labor costs and time-intensive tasks, making high-quality creative work more accessible.
- Democratization of Creation: Anyone with access to AI tools can now try their hand at music composition or art creation, regardless of their background or skill level. This opens up creative opportunities for people who might not have had the resources or training to pursue traditional methods.
- Enhanced Creativity: AI provides artists and musicians with new ideas and perspectives. It can suggest innovative designs, melodies, or compositions that a human artist might not have considered, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
AI in art and music is not about replacing human creativity; rather, it’s about enhancing it, offering new ways for creators to express themselves and push the boundaries of traditional creative fields.
Here's a more detailed version of sections 7 and 8:
7. Deep Learning in Interactive Storytelling
AI is transforming storytelling by enabling dynamic, interactive narratives that can change based on the audience's decisions. This is making the storytelling process more immersive and personalized, especially in gaming and films.
Use in Games and Films
- Interactive Games: Video games like Detroit: Become Human use AI-driven narrative engines to adjust the storyline based on player choices. Each decision a player makes can lead to a completely different outcome, allowing players to shape the narrative. This dynamic form of storytelling creates a more personalized gaming experience.
- AI-Generated Story Arcs and Dialogues: In addition to altering storylines, AI can generate entire story arcs and dialogue trees. These AI systems analyze the player's actions and reactions, allowing the game or film to craft new, tailored content that feels organic and responsive to the player.
Future Potential of AI in Storytelling
- Choose-Your-Own-Adventure Movies: With advancements in AI, movies could one day allow audiences to choose their path, similar to interactive games. Imagine watching a film where you, as the viewer, decide the protagonist's choices and determine the story's direction. AI could analyze your decisions in real-time to craft new scenes and dialogues that reflect your preferences.
- Personalized Endings or Plot Twists: AI could also alter the ending or introduce plot twists based on the viewer’s history and preferences. For instance, a movie might change its outcome depending on how much action, drama, or romance you’ve watched in the past. The film could adapt to provide an ending that resonates with your tastes.
This level of interactivity and personalization would make entertainment feel alive, constantly evolving with the viewer or player’s choices.
8. Ethical Challenges and Concerns
While AI is revolutionizing the entertainment industry, it also raises several ethical concerns that need to be addressed.
Deepfakes and Misinformation
- Deepfake Technology: One of the most controversial uses of AI in entertainment is deepfake technology, which can create hyper-realistic videos or images that depict people saying or doing things they never did. This has significant implications for misinformation and fake news. The ability to manipulate videos to the point where they are indistinguishable from reality poses a serious challenge for authenticity and truth in media.
- Copyright Infringement: AI tools can also be used to replicate art, music, or movies without the consent of the creators, leading to concerns about intellectual property rights. For example, AI can be used to replicate an artist's style, creating new content that mimics their work. This can infringe on the rights of creators and dilute the value of original art.
Job Displacement
- Automation in Creative Roles: As AI becomes more capable of generating art, music, and stories, there’s a growing concern that automation could replace human creative roles. Tasks like graphic design, music composition, and even scriptwriting could be automated, leading to job losses for creatives who depend on these skills for their livelihoods.
- New Opportunities in AI: However, AI is also creating new opportunities. As AI systems need to be designed, maintained, and improved, new jobs are emerging in fields like AI design, maintenance, and human-AI collaboration. These roles offer opportunities for creative professionals to work alongside AI, ensuring that its potential is fully harnessed while mitigating some of the displacement effects.
Data Privacy
- Recommendation Engines: As AI systems collect vast amounts of personal data to provide personalized experiences, privacy issues become a major concern. Platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube track user behavior to offer tailored content, but this data can be misused or accessed by third parties without consent. Users might not always be aware of how much personal data is being collected and how it’s being used, leading to questions about data ownership and security.
- Ethical Data Use: To protect users, AI systems must be designed with ethical data practices in mind, ensuring transparency in how data is collected, stored, and shared. Regulatory measures, like data protection laws (e.g., GDPR), are crucial for ensuring that users' privacy rights are upheld while still allowing for personalized content.
As AI continues to evolve in entertainment and creative fields, its potential for personalized, immersive experiences is immense, but it’s essential to navigate the ethical challenges it brings. Balancing innovation with responsible AI use will be key to harnessing the technology's benefits while protecting creators and consumers.
Conclusion
AI is not just enhancing the entertainment experience—it’s redefining the boundaries of imagination and interactivity. From smarter games and stunning visuals to personalized content and creative collaboration, AI continues to transform how stories are told and experienced.




.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)