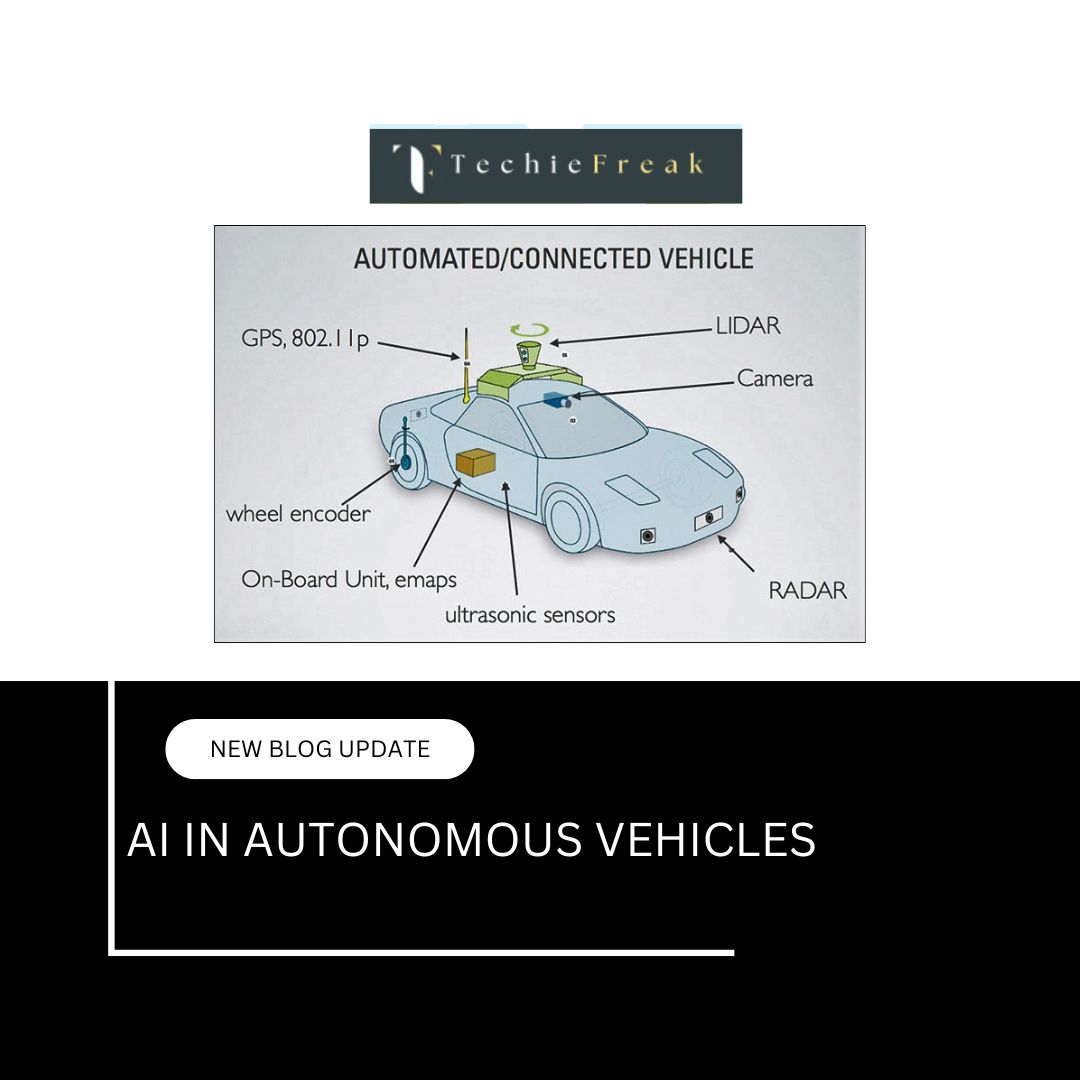
Driving the Future – AI in Autonomous Vehicles
Introduction
Self-driving cars, once a futuristic concept from science fiction, are becoming a reality thanks to Artificial Intelligence (AI). These autonomous vehicles (AVs) are equipped with cutting-edge AI systems that allow them to perceive the environment, make decisions, and navigate roads with minimal human input. As the automotive industry shifts gears, AI is at the center of this transformation, promising safer roads, lower emissions, and smarter transportation.
This blog explores how AI drives the autonomous vehicle revolution, covering everything from perception and decision-making to real-world use cases and ethical challenges.
Here’s a detailed and enriched version of your write-up on AI in autonomous vehicles, with clearer structure, deeper insights, and more engaging flow:
How AI Powers Self-Driving Cars: The Brain Behind Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are no longer just futuristic concepts—they’re operating on real roads today. At the heart of these intelligent machines is Artificial Intelligence, functioning as the brain that interprets data, makes decisions, and ensures safety. Let’s dive deeper into how AI enables self-driving cars to navigate complex real-world environments.
1. AI as the Brain of Self-Driving Cars
AI mimics human cognition in self-driving systems. It processes data from multiple sensors in real time, makes decisions, and continuously learns from driving experiences.
Key Technologies Involved:
Computer Vision
- Enables the vehicle to "see" its environment.
- Recognizes objects like pedestrians, traffic lights, stop signs, cyclists, and lane markings.
- Real-time image analysis helps maintain lane discipline and avoid obstacles.
Sensor Fusion
- AVs are equipped with a combination of LIDAR, Radar, Cameras, GPS, and Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs).
- AI algorithms combine this data to create a unified, 360° view of the surroundings—essential for depth perception and spatial awareness.
Deep Learning
- Neural networks are trained on millions of miles of driving data.
- These models can learn and replicate human driving behavior, from merging lanes to responding to unpredictable events (like a child running onto the street).
Real-World Example:
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet (Google's parent company), is a global leader in autonomous driving. It:
- Uses deep neural networks to interpret sensor data.
- Leverages high-definition maps and real-time traffic data.
- Operates fully autonomous taxi services in cities like Phoenix, Arizona.
2. Perception and Environment Mapping
To drive safely, AVs must perceive their environment with precision and anticipate how it might change.
How It Works:
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- Emits rapid laser pulses to measure distances with centimeter-level accuracy.
- Generates detailed 3D maps of surroundings.
- Crucial for detecting edges, curbs, and static or moving objects.
Radar
- Measures the speed and position of surrounding vehicles and objects.
- Especially useful in poor weather conditions (rain, fog) where cameras and LIDAR might struggle.
- Helps detect distant or fast-moving objects.
Cameras
- Offer high-resolution visual input.
- Detect color-coded signs (like red traffic lights), lane markings, turn indicators, hand gestures, and more.
- Can interpret human cues, such as eye contact or body language at crosswalks.
AI’s Role in Perception:
- Image Recognition: Deep learning algorithms classify and detect objects like vehicles, traffic lights, and pedestrians.
- Behavior Prediction: AI forecasts the likely path of nearby objects—will a pedestrian cross or wait? Is a cyclist turning left?
- Semantic Segmentation: Identifies road vs. sidewalk vs. vegetation for path planning.
Use Case: Tesla’s Autopilot
- Relies on 8 surround cameras, 12 ultrasonic sensors, and a custom AI chip.
- Provides semi-autonomous features like auto lane change, adaptive cruise control, and self-parking.
- Uses over-the-air updates to constantly improve its AI driving model based on fleet learning.
Here's your expanded and detailed version of sections 3 and 4, aligned with the depth and tone of the previous content:
3. Path Planning and Decision Making
Once an autonomous vehicle (AV) perceives its surroundings, the next critical task is making decisions—how to move, where to go, and how to respond to dynamic elements on the road. This phase is where AI transitions from observation to action.
Key Capabilities:
Path Planning
- Involves determining the most efficient and safe route from the vehicle’s current location to its destination.
- Factors include traffic data, road conditions, speed limits, lane availability, and detours.
Motion Planning
- Focuses on how the vehicle moves along the chosen path.
- AI systems calculate when to accelerate, brake, or steer, ensuring smooth and collision-free movement.
AI’s Role in Decision-Making:
- Reinforcement Learning: AI agents are trained through trial and error to make real-time driving decisions in complex environments.
- Predictive Modeling: AI anticipates future movements of nearby vehicles, pedestrians, or cyclists and adjusts plans accordingly.
- Multi-Agent Coordination: In traffic, AI enables the AV to account for the behavior of multiple road users simultaneously, including merging, yielding, and navigating intersections.
Real-World Example:
Uber’s autonomous vehicle program integrated AI to navigate busy city environments, where split-second decisions are required. The system learned to avoid erratic drivers, recognize jaywalkers, and manage unpredictable road scenarios like construction zones or temporary lane changes.
4. Real-World Applications and Trials
Autonomous vehicles have progressed far beyond prototypes and lab simulations. Across the globe, several companies are actively deploying or testing AI-powered vehicles in real-world environments.
Notable Programs:
Waymo One
- Operated by Alphabet’s Waymo, this service offers fully autonomous taxi rides to the public in Phoenix, Arizona.
- Vehicles operate without a safety driver, relying entirely on AI to navigate suburban streets and traffic.
Cruise
- Backed by General Motors, Cruise has been testing self-driving taxis in San Francisco, focusing on night operations and densely populated urban environments.
- The vehicles are designed to handle complex traffic, pedestrian crossings, and variable lighting conditions.
Nuro
- Specializes in autonomous delivery. Its compact driverless pods are designed to carry groceries, parcels, and pharmacy items in residential neighborhoods.
- The focus is on short-distance logistics, reducing delivery costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles:
- Enhanced Safety: The majority of road accidents are due to human error—distraction, fatigue, or impaired driving. AI eliminates these factors, enabling precise and consistent decision-making.
- Greater Accessibility: AVs provide mobility solutions for people who are elderly, visually impaired, or unable to drive due to physical disabilities.
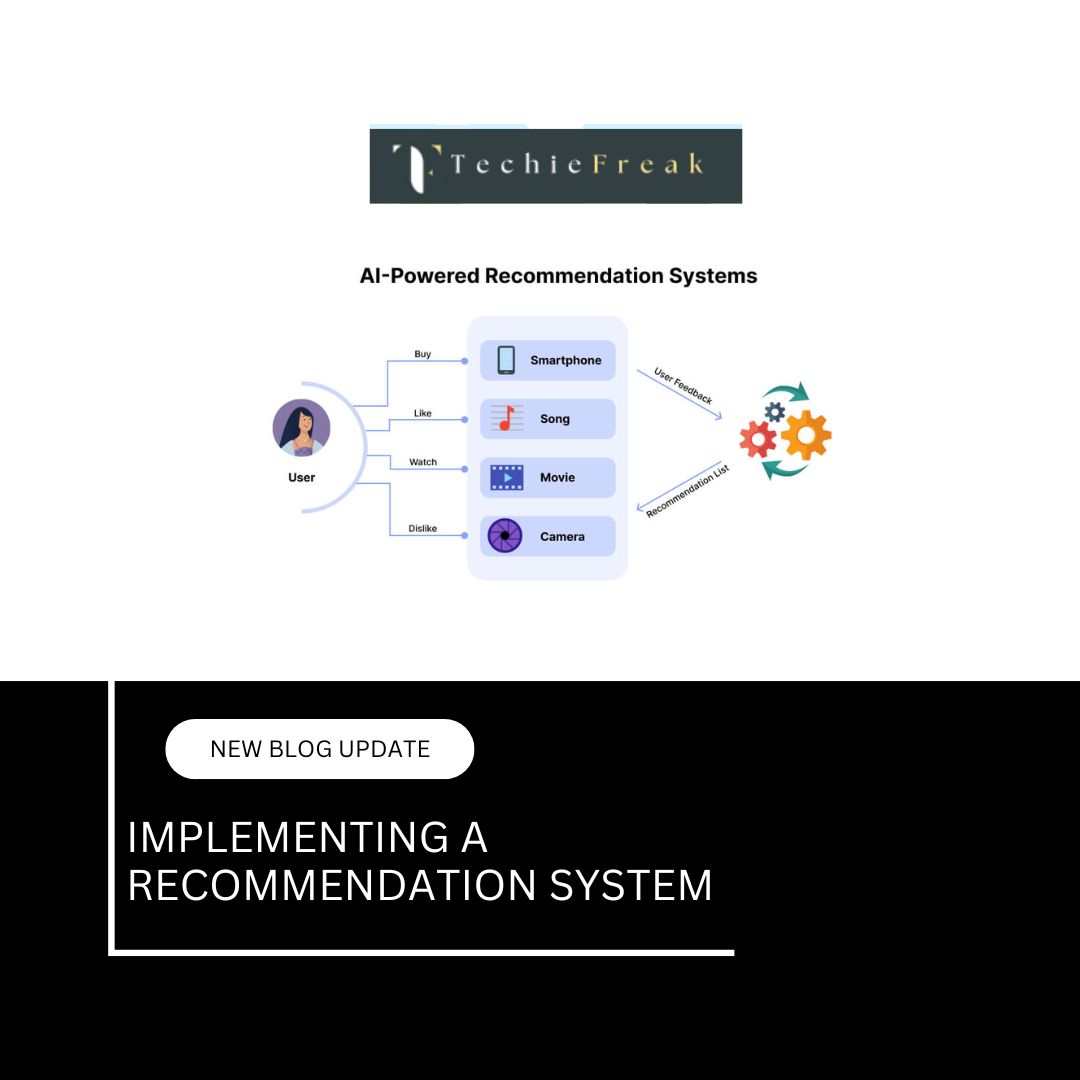
- Traffic and Fuel Efficiency: AI can optimize routes to avoid congestion, reduce idle times, and ensure smoother traffic flow, resulting in lower emissions and fuel consumption.
Here’s the expanded and more detailed version of sections 5 and 6, keeping the tone consistent with the rest of the blog and enhancing the depth of content:
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite significant technological strides, the road to fully autonomous vehicles is far from smooth. As AVs become more integrated into society, they introduce complex challenges that go beyond just engineering.
Safety and Reliability
Autonomous systems must be capable of handling highly unpredictable and non-standard driving conditions, such as:
- Aggressive or erratic human drivers
- Sudden obstacles or road debris
- Adverse weather like heavy rain, snow, or fog that can impair sensors
While AI performs well under controlled environments, ensuring consistent safety in real-world, high-risk situations remains an ongoing challenge.
Ethical Dilemmas
AI systems in AVs may face split-second moral decisions. Consider:
- If an accident is inevitable, should the car prioritize the lives of passengers or pedestrians?
- How should AI weigh risk to property vs. risk to human life?
These questions underscore the lack of a universal ethical framework for machine decision-making. Philosophers, technologists, and policymakers are still debating how to program these values into autonomous systems.
Data Privacy and Security
AVs generate and transmit enormous amounts of data—from GPS location and camera footage to personal driver preferences and biometric data.
- Who owns this data—the user, the manufacturer, or the service provider?
- How can this data be protected from cyberattacks or misuse?
Regulatory bodies are calling for stricter data protection laws tailored specifically to autonomous technologies.
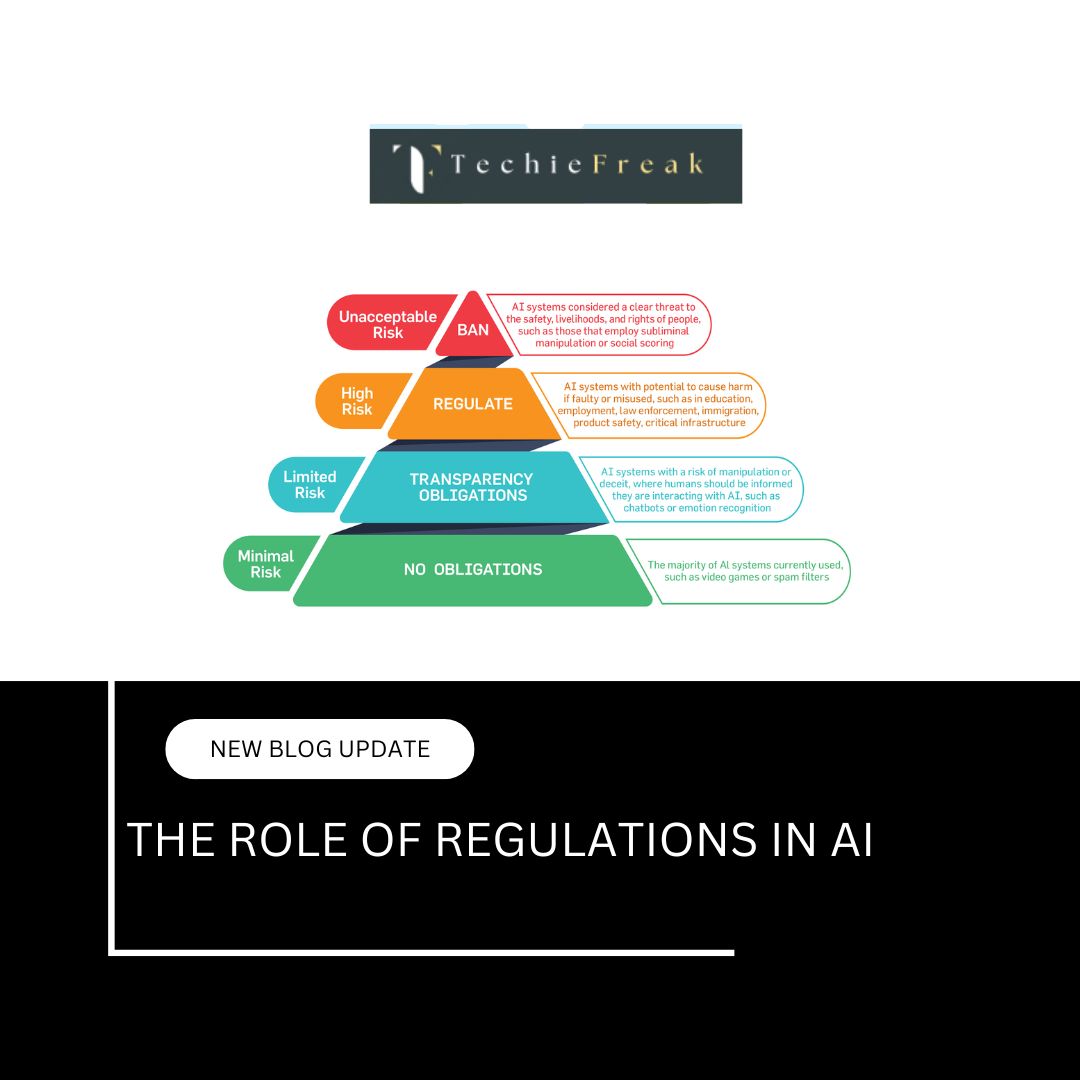
Legal and Regulatory Barriers
Autonomous vehicles must adhere to traffic laws, which vary significantly across countries and even cities. Moreover:
- Some regions allow AV testing with safety drivers, while others demand full remote control capabilities.
- The lack of standardized international regulations makes it difficult for manufacturers to scale globally.
As governments work to catch up, AV developers must constantly update systems to remain compliant with changing legal landscapes.
6. The Road Ahead: Future of Autonomous Vehicles
The journey to full autonomy is a marathon, not a sprint. While we have already reached Level 2 and Level 3 autonomy in many commercial models, true self-driving vehicles (Level 5) are still in development.
What’s on the Horizon:
Level 5 Autonomy
- AVs that require no human intervention at all—no steering wheel, pedals, or manual override.
- Can operate in all environments, from dense urban cities to remote rural areas.
- Still undergoing extensive real-world testing due to technological and regulatory limitations.
5G and V2X Communication
- 5G allows ultra-fast, low-latency communication between vehicles (Vehicle-to-Vehicle or V2V) and infrastructure (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure or V2I).
- Enables smart traffic lights, coordinated lane merging, and real-time accident alerts.
- V2X helps AVs make better decisions by seeing beyond their immediate sensor range.
Edge AI
- Instead of relying entirely on cloud servers, Edge AI allows AVs to process data directly on the vehicle, reducing response time and dependency on internet connectivity.
- Critical for making split-second decisions, especially in areas with poor network coverage.
Impact on Society:
- Redefinition of public transport
- New job roles in AI model monitoring and AV maintenance
- Changes in urban planning (e.g., fewer parking lots)
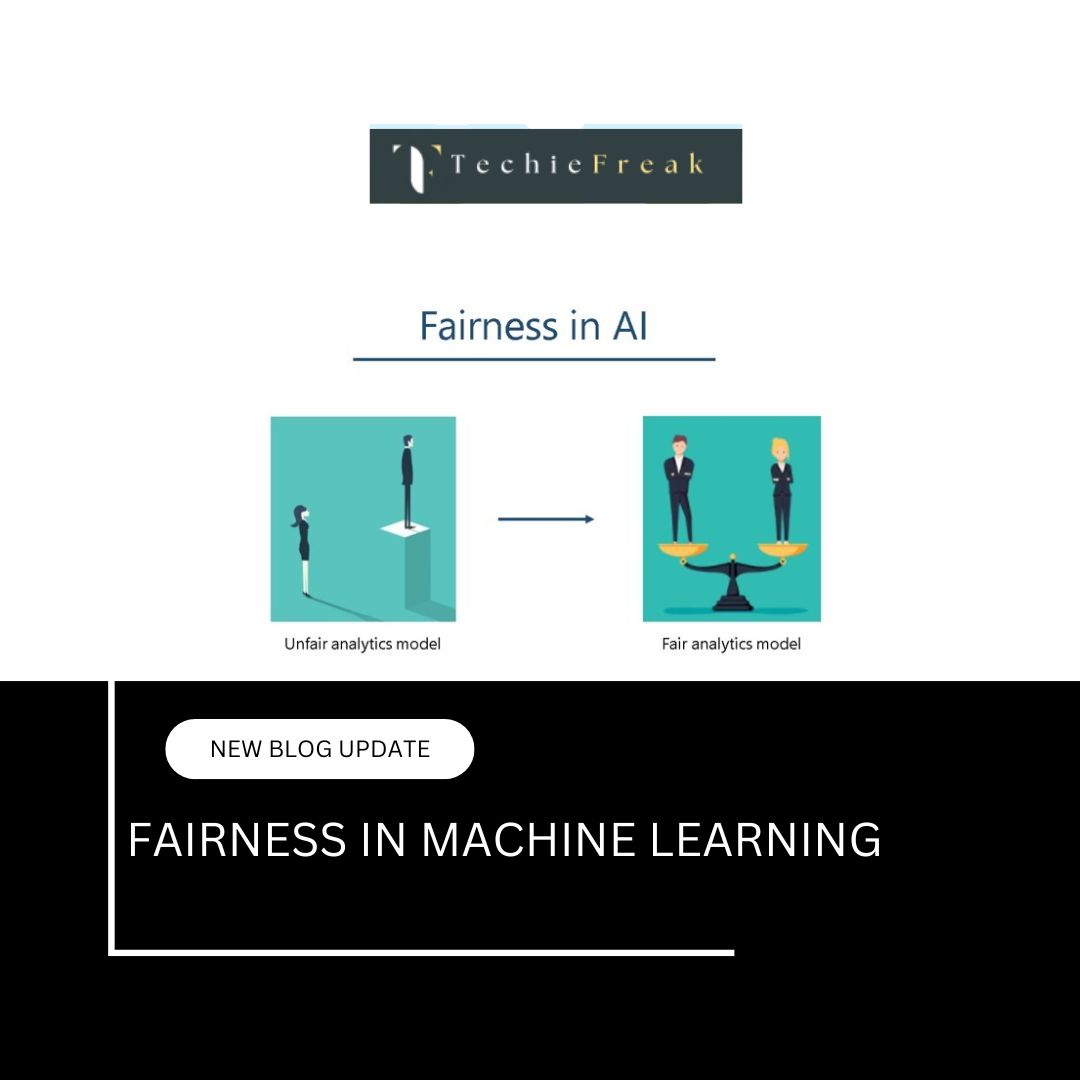
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is the cornerstone of autonomous vehicle innovation. By mimicking human perception, decision-making, and control, AI enables cars to navigate the world more safely and efficiently. While challenges remain, ongoing advances in AI algorithms, computing power, and sensor technology are steering us toward a driverless future.
As industries, governments, and tech companies collaborate, the dream of safe, smart, and sustainable mobility is fast becoming a reality. Autonomous vehicles powered by AI are not just transforming how we travel—they're redefining the very idea of transportation.



.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)