The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Combating Climate Change
Climate change stands as a defining global challenge, threatening natural ecosystems, human health, food security, and economic stability. Scientific consensus confirms that urgent action is required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and build resilience against climate impacts. In this context, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a transformative tool with the potential to accelerate climate action through enhanced data processing, prediction, optimization, and automation.
AI’s role in climate change spans multiple domains — from refining climate models to optimizing energy systems, enabling precision monitoring, and supporting informed policymaking. This document explores these applications in detail.
1. AI for Advanced Climate Modeling and Prediction
Understanding and forecasting climate dynamics is foundational for effective action. Traditional climate models, while powerful, are computationally intensive and sometimes limited in their spatial and temporal resolution.
AI enhances climate science in the following ways:
- Processing Big Climate Data: AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, can analyze petabytes of data collected from satellites, weather stations, ocean buoys, and climate sensors. This allows researchers to detect patterns and anomalies that may not be visible through traditional methods.
- Improving Forecast Accuracy: Machine learning models are now capable of forecasting short-term weather events (like storms and heatwaves) and long-term climate patterns (such as El Niño events) with improved accuracy.
- Downscaling Climate Projections: AI aids in “downscaling” global climate models to produce localized forecasts, which are crucial for regional planning and adaptation measures.
For example, Google's DeepMind has developed machine learning models that can predict rainfall with greater precision, benefiting disaster preparedness and agricultural planning.
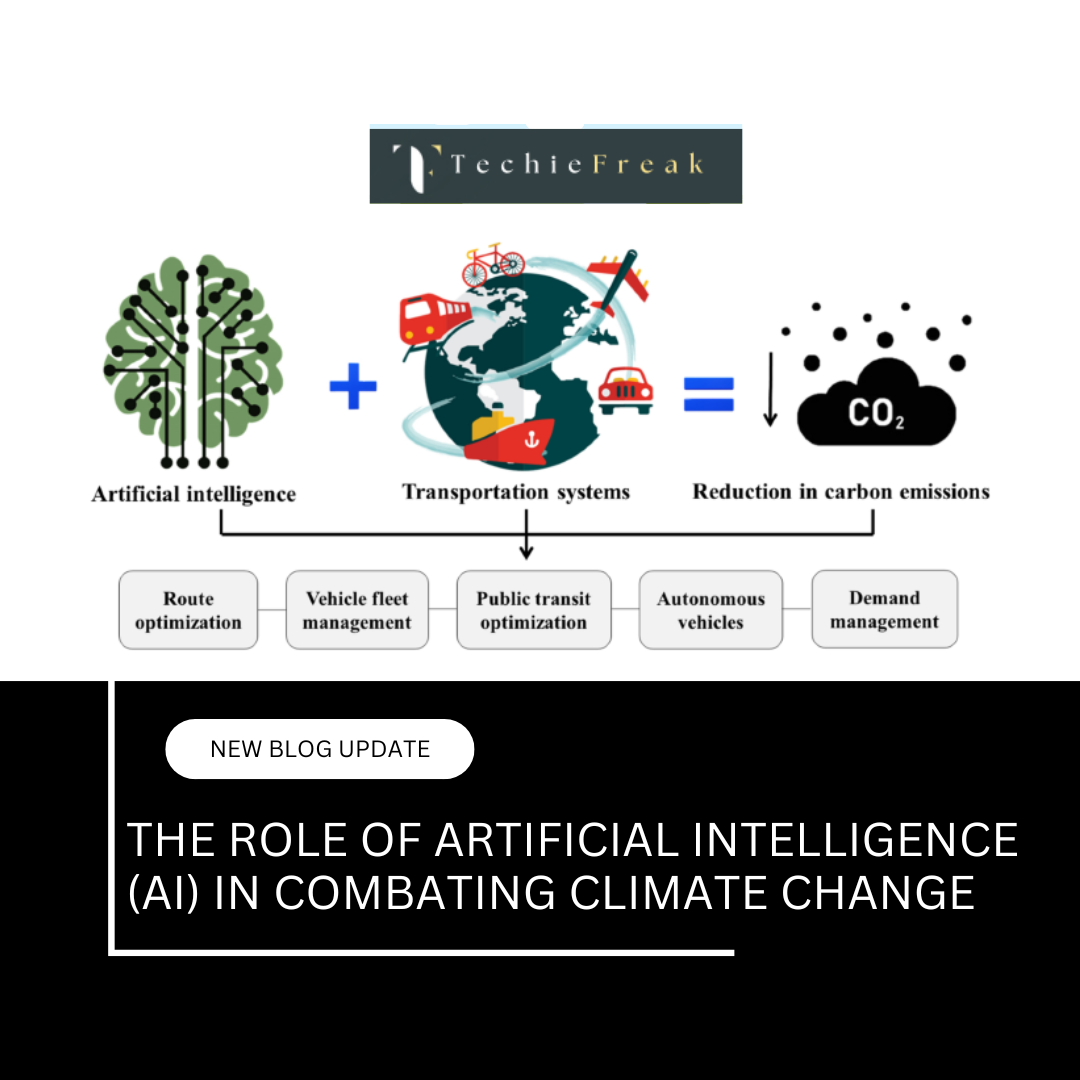
2. AI in Energy Efficiency and Decarbonization
The energy sector is the largest contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions. AI offers significant potential to reduce emissions by optimizing the production, distribution, and consumption of energy.
- Smart Grid Management: AI algorithms balance electricity supply and demand in real-time, facilitating the integration of variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Smart grids minimize energy loss and improve reliability.
- Building Energy Optimization: AI-enabled systems control heating, cooling, and lighting in buildings, reducing energy use without compromising comfort. Automated energy management systems are now being deployed in residential and commercial buildings worldwide.
- Industrial Process Optimization: In energy-intensive industries such as steel, cement, and chemicals, AI helps optimize operations, reduce fuel consumption, and cut emissions.
For instance, Siemens and other engineering firms have implemented AI-based predictive maintenance systems that identify inefficiencies and equipment failures early, preventing energy wastage.
3. Facilitating Renewable Energy Integration
Renewable energy is vital for decarbonization but poses challenges due to its intermittent nature. AI addresses this by:
- Forecasting Renewable Output: Machine learning models predict solar and wind energy production based on weather conditions, enabling better grid planning.
- Optimizing Energy Storage: AI determines the best times to store energy in batteries and when to release it, ensuring a stable energy supply even when renewables fluctuate.
- Enhancing Grid Stability: By forecasting energy demand and generation, AI helps utilities maintain balance and prevent blackouts.
Countries leading in renewable energy, such as Germany and Denmark, are increasingly reliant on AI to manage their energy transitions effectively.
4. Environmental Monitoring and Natural Ecosystem Protection
Preserving forests, oceans, and other natural systems is critical to climate mitigation, as they serve as carbon sinks. AI supports these efforts through enhanced monitoring and management:
- Deforestation Detection: Satellite imagery analyzed by AI can detect illegal logging and land-use changes in near real-time, enabling faster enforcement.
- Glacier and Ice Monitoring: AI models track the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps, providing data essential for understanding sea-level rise.
- Biodiversity Monitoring: AI-powered acoustic sensors and camera traps identify species in remote regions, helping conservationists monitor wildlife populations and ecosystem health.
Organizations like Global Forest Watch employ AI technologies to alert governments and NGOs about deforestation hotspots, contributing to more effective climate action.
5. AI-Enhanced Carbon Capture and Emission Reduction
Reducing emissions from heavy industries and existing infrastructure is crucial. AI contributes by:
- Optimizing Carbon Capture Technologies: AI improves the efficiency of carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems by analyzing operational data and identifying optimal capture conditions.
- Industrial Emission Control: Factories use AI models to minimize emissions during manufacturing processes by adjusting variables in real-time.
- Tracking Emission Sources: AI systems analyze satellite imagery and sensor networks to monitor emissions at national and corporate levels, ensuring transparency and accountability.
For example, Carbon Mapper, a coalition of research institutions, uses AI-driven satellite data to detect methane leaks globally — a significant contributor to climate change.
6. AI in Climate Finance and Sustainable Investment
The financial sector plays a key role in funding the transition to a low-carbon economy. AI supports climate finance by:
- Assessing Climate Risks: AI models evaluate physical risks (e.g., flooding, wildfires) and transition risks (e.g., policy changes) for businesses and infrastructure projects.
- Enabling Green Investments: Investors use AI to analyze environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, identifying sustainable investment opportunities.
- Supporting Carbon Markets: AI tracks carbon credits and offsets, ensuring that climate finance mechanisms are credible and efficient.
Climate fintech startups are using AI to design climate risk dashboards for banks, insurers, and asset managers.
7. AI for Climate Adaptation and Disaster Resilience
Beyond mitigation, societies must adapt to unavoidable climate impacts. AI enhances resilience through:
- Disaster Early Warning Systems: AI predicts natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes, and wildfires, enabling early evacuation and preparation.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: AI provides farmers with weather forecasts, soil analysis, and crop recommendations, improving food security amid changing climatic conditions.
- Urban Planning: Cities use AI to model future climate risks and design infrastructure that is resilient to heatwaves, flooding, and sea-level rise.
Projects like IBM's Green Horizon are using AI to help cities plan for climate risks and reduce pollution levels.
8. Challenges and Limitations of AI in Climate Action
While AI offers promising solutions, several challenges must be addressed:
- Energy Consumption of AI Systems: Training large AI models requires significant computing power, leading to increased energy use and associated emissions.
- Data Gaps: AI relies on high-quality, representative data, which may be lacking in developing countries and remote regions.
- Equity and Access: AI-driven climate solutions risk exacerbating inequalities if benefits are concentrated in technologically advanced nations while vulnerable populations are left behind.
- Ethical and Governance Issues: The deployment of AI in climate action must ensure transparency, accountability, and public trust.
Sustainable AI development practices, including the use of green data centers and efficient algorithms, are essential to mitigate these concerns.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is becoming an indispensable ally in the global fight against climate change. Its ability to process massive datasets, generate predictive insights, and optimize complex systems makes AI a powerful tool for both climate mitigation and adaptation. From transforming energy systems and protecting natural ecosystems to enhancing disaster preparedness and guiding sustainable investments, AI's applications are diverse and far-reaching.
However, the successful integration of AI in climate action requires careful attention to challenges related to energy consumption, data equity, and governance. By addressing these issues, AI can fulfill its potential as a key enabler of a sustainable and resilient future.
Next Blog- AI Research Frontiers



.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)