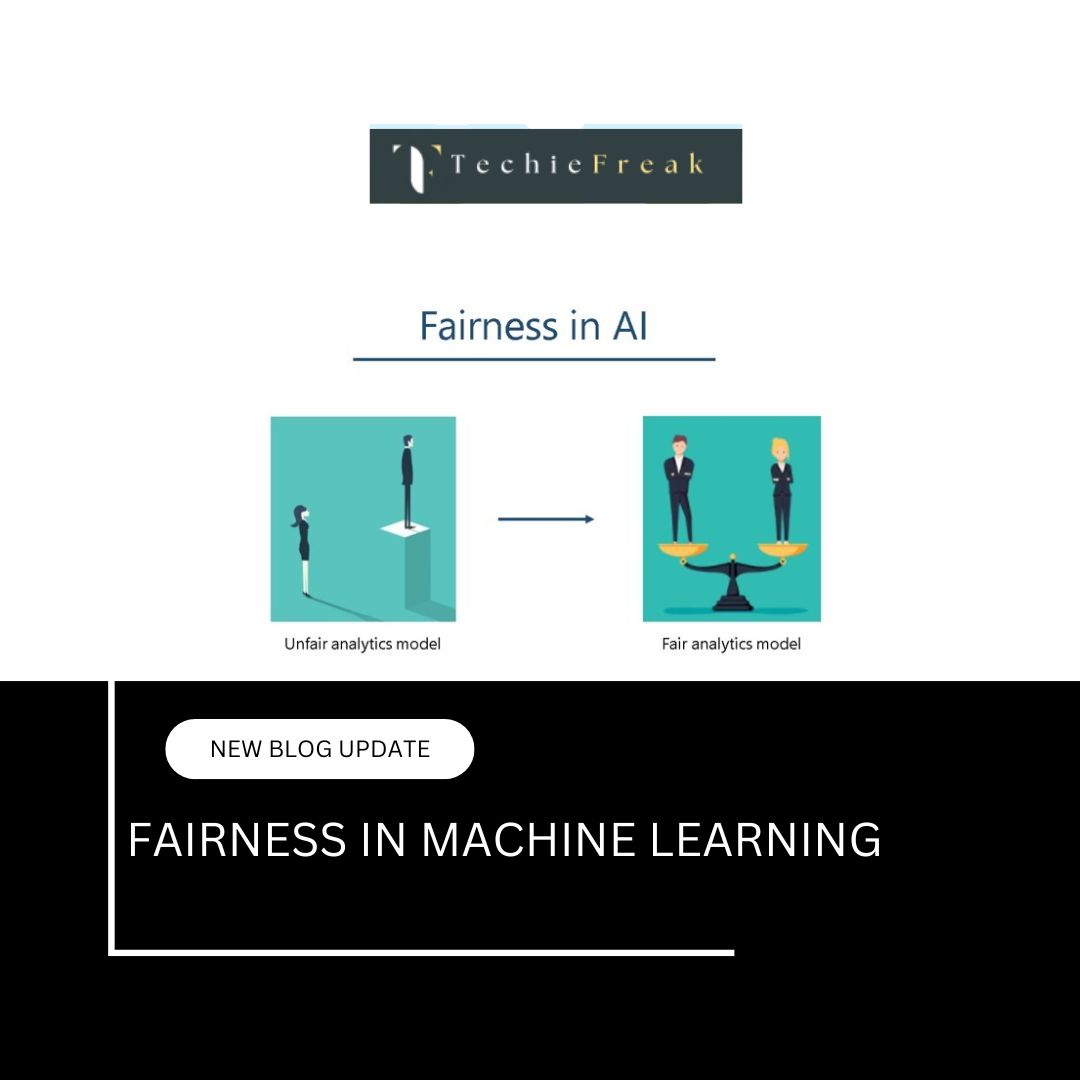
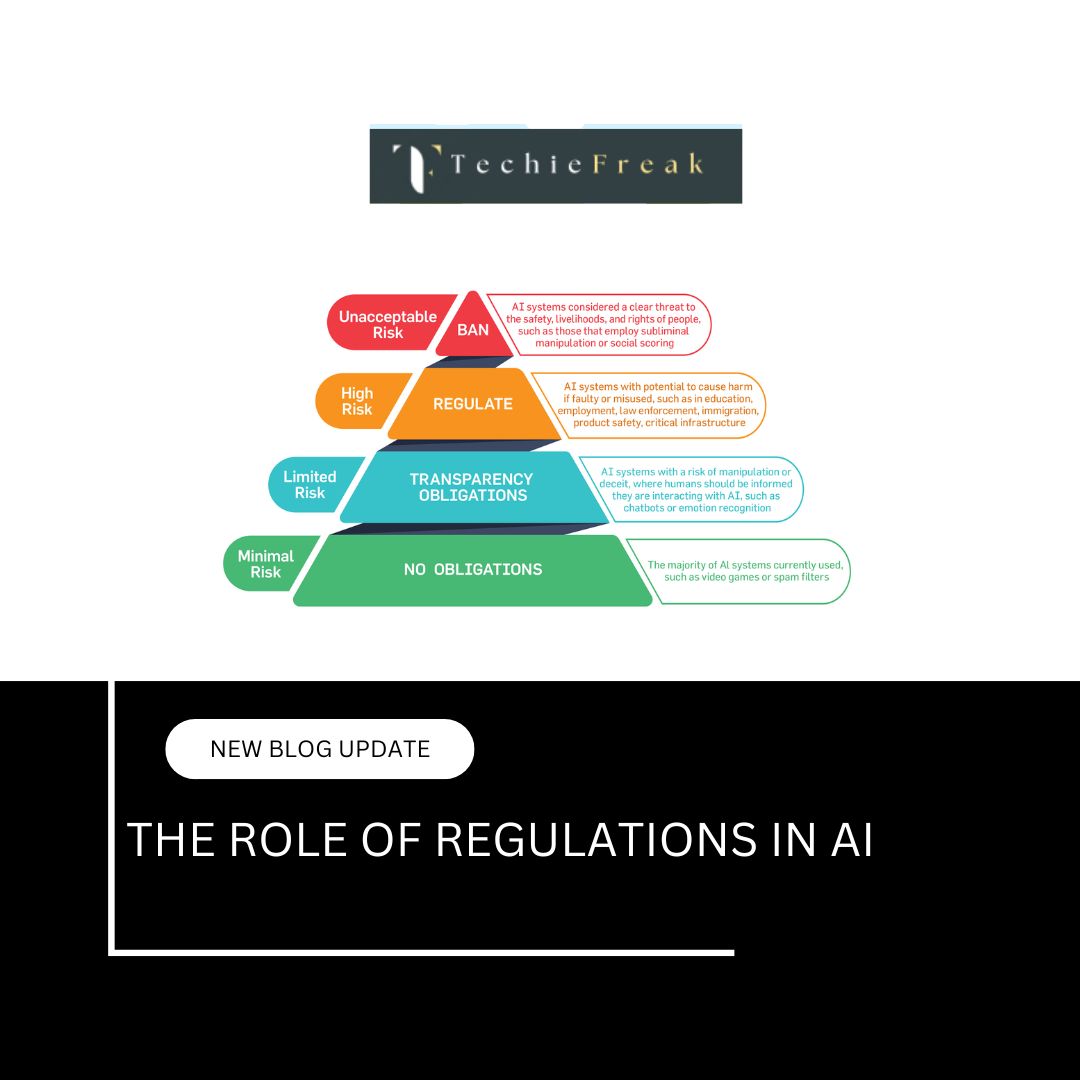
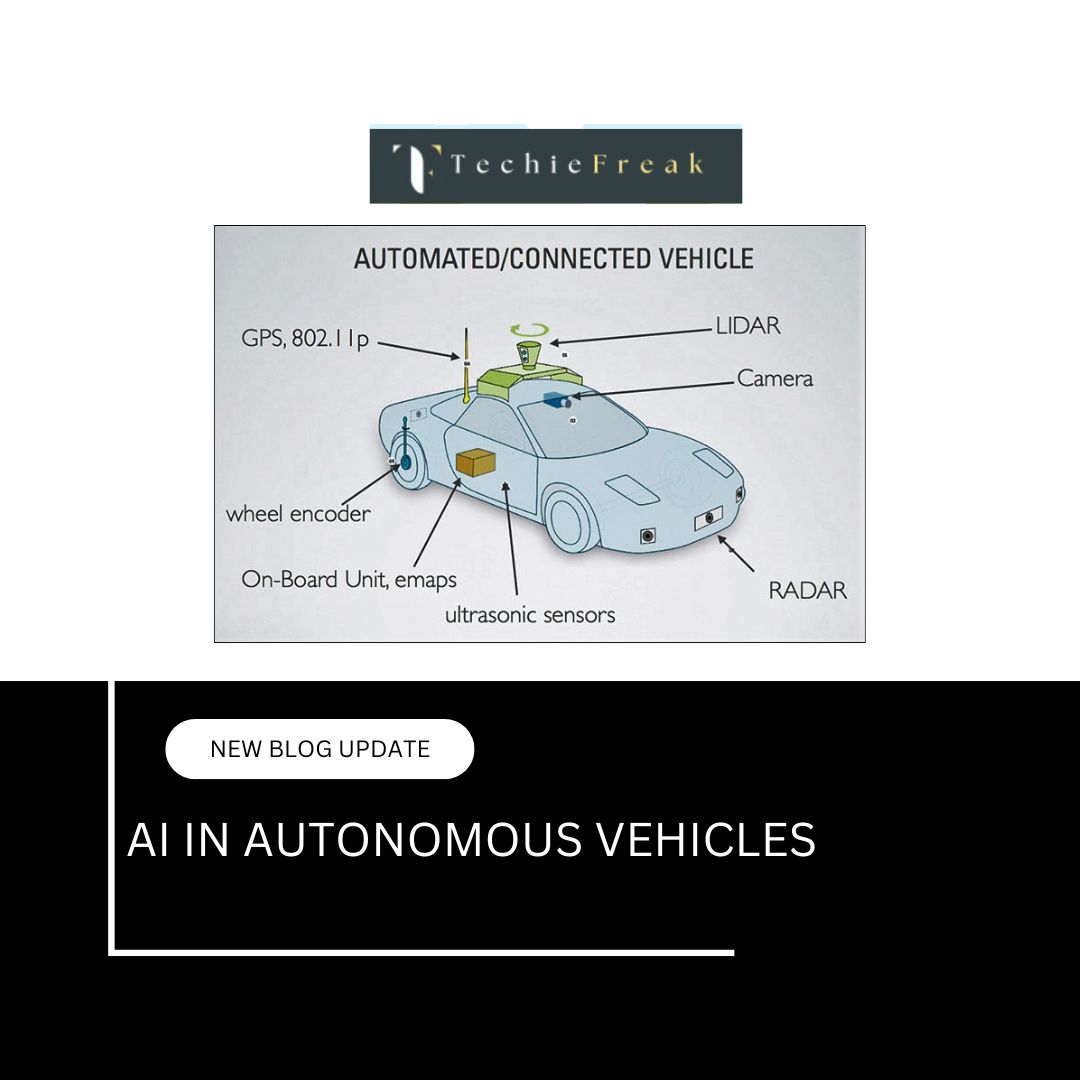
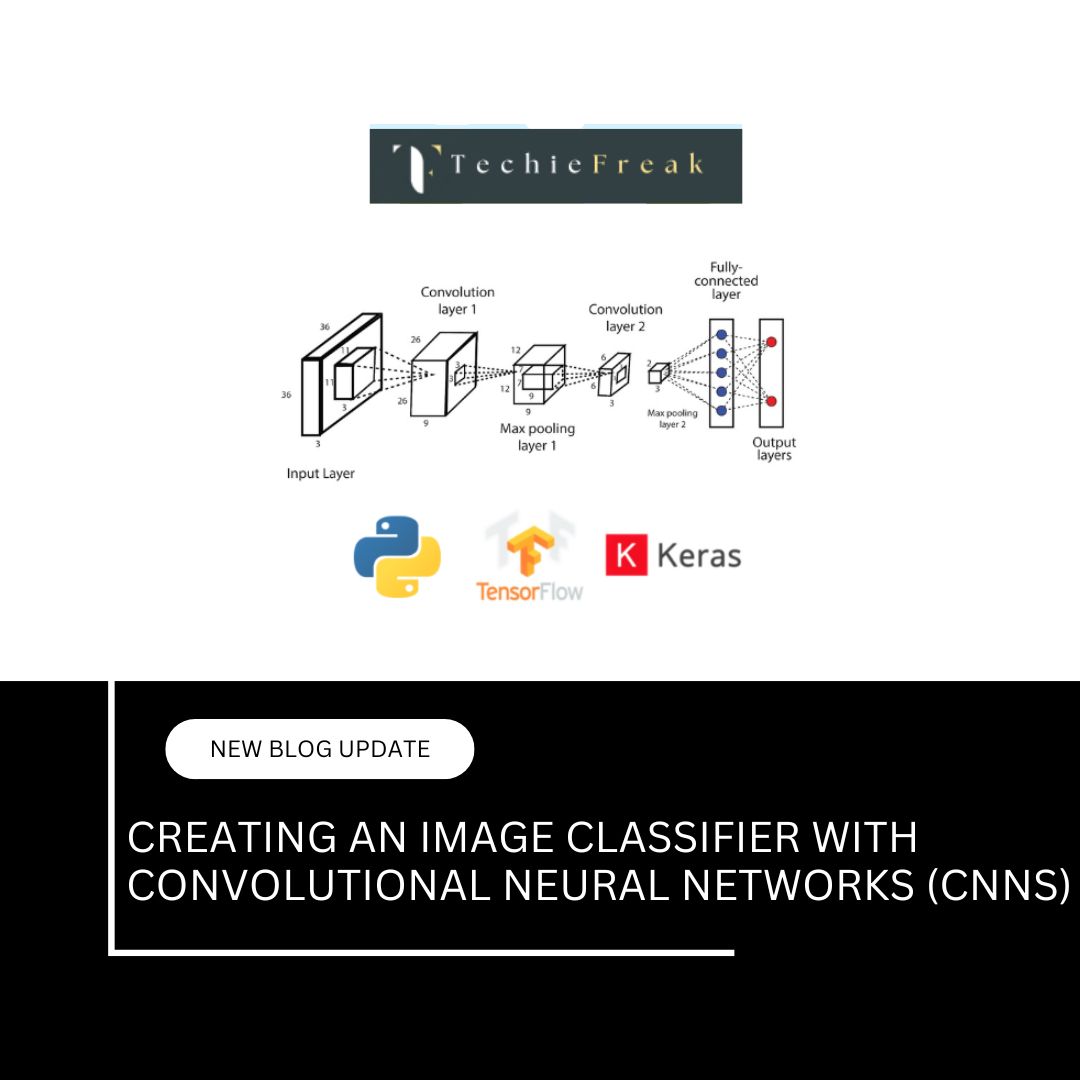
AI and the Job Market
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping industries and the global economy at a rapid pace. Its influence on the job market is both transformative and complex, bringing significant opportunities as well as challenges. As AI systems evolve, they impact employment patterns, skill requirements, and workforce structures across various sectors.
1. Job Displacement due to Automation
One of the most discussed impacts of AI is its potential to automate tasks traditionally performed by humans. Repetitive and routine jobs, especially in sectors like manufacturing, transportation, customer service, and data entry, are increasingly being handled by AI-driven systems and robots.
For example:
- Automated customer service chatbots are replacing call center operators.
- AI algorithms are used in factories for predictive maintenance and assembly line automation.
- Autonomous vehicles threaten to reduce the need for human drivers in logistics and transportation.
Studies by institutions like the World Economic Forum suggest that millions of jobs may be displaced in the coming years as AI and automation continue to expand.
2. Creation of New Job Roles
While AI leads to job displacement in certain sectors, it also creates new roles that did not exist before. The rise of AI has increased demand for professionals such as:
- Machine learning engineers
- Data scientists
- AI ethicists
- Robotics technicians
- AI trainers
In addition, sectors like healthcare, finance, and marketing are witnessing the emergence of hybrid roles where professionals are expected to work alongside AI tools, interpreting and validating AI-generated outcomes.
3. Evolution of Existing Jobs
AI is not only eliminating jobs but also transforming existing ones. Many professions are experiencing a shift in required skills as AI tools are integrated into daily workflows. For instance:
- Financial analysts now use AI-powered tools for risk assessment and fraud detection.
- Doctors leverage AI for diagnostic support, analyzing medical images and patient data.
- Marketers use AI to optimize campaigns through predictive analytics and personalized targeting.
In these cases, AI acts as an augmentative tool, enhancing human productivity rather than replacing it entirely.
4. Skills Gap and Workforce Readiness
The growing integration of AI into businesses is creating a skills gap in the labor market. While technical skills such as coding, data analysis, and AI model training are in high demand, there is also an increased need for soft skills that AI cannot replicate effectively, such as critical thinking, creativity, leadership, and emotional intelligence.
Educational institutions and corporate training programs are now focusing on reskilling and upskilling workers to prepare them for an AI-driven economy. Lifelong learning has become essential to maintain career resilience.
5. Sector-Specific Impacts
The effects of AI on employment vary significantly across different sectors:
- Manufacturing: High automation risk; however, increased demand for engineers and maintenance experts.
- Healthcare: Job growth in AI-assisted diagnostics, telemedicine, and health informatics.
- Finance: Automation of routine processes but increased roles in regulatory compliance and AI oversight.
- Retail and E-commerce: Automated inventory management and customer interaction, coupled with new roles in AI system management.
6. Geopolitical and Socioeconomic Considerations
The adoption of AI is also deepening divides between countries and socioeconomic classes. Advanced economies with strong technological infrastructure are better positioned to benefit from AI, while developing nations may face greater challenges due to limited resources for workforce transformation.
Within countries, workers in low-skill, routine jobs are at higher risk of displacement, whereas those in creative and strategic roles are more likely to benefit from AI augmentation.
7. Policy and Governance
To manage AI’s impact on employment, policymakers are exploring various strategies:
- Implementing social safety nets for displaced workers
- Promoting public and private investment in skills development
- Encouraging ethical AI practices to prevent discriminatory automation
- Considering regulatory frameworks for responsible AI deployment
International organizations and governments are actively studying the long-term implications of AI to formulate policies that support inclusive growth.
Conclusion
AI is fundamentally altering the landscape of the global job market. While it brings about job displacement in certain sectors, it simultaneously creates new opportunities and transforms existing roles. The key challenge for societies is to manage this transition effectively by investing in education, reskilling, and policies that support workers through the evolving demands of the AI era. Success in this endeavor will determine whether AI becomes a force for inclusive prosperity or a driver of social inequality.
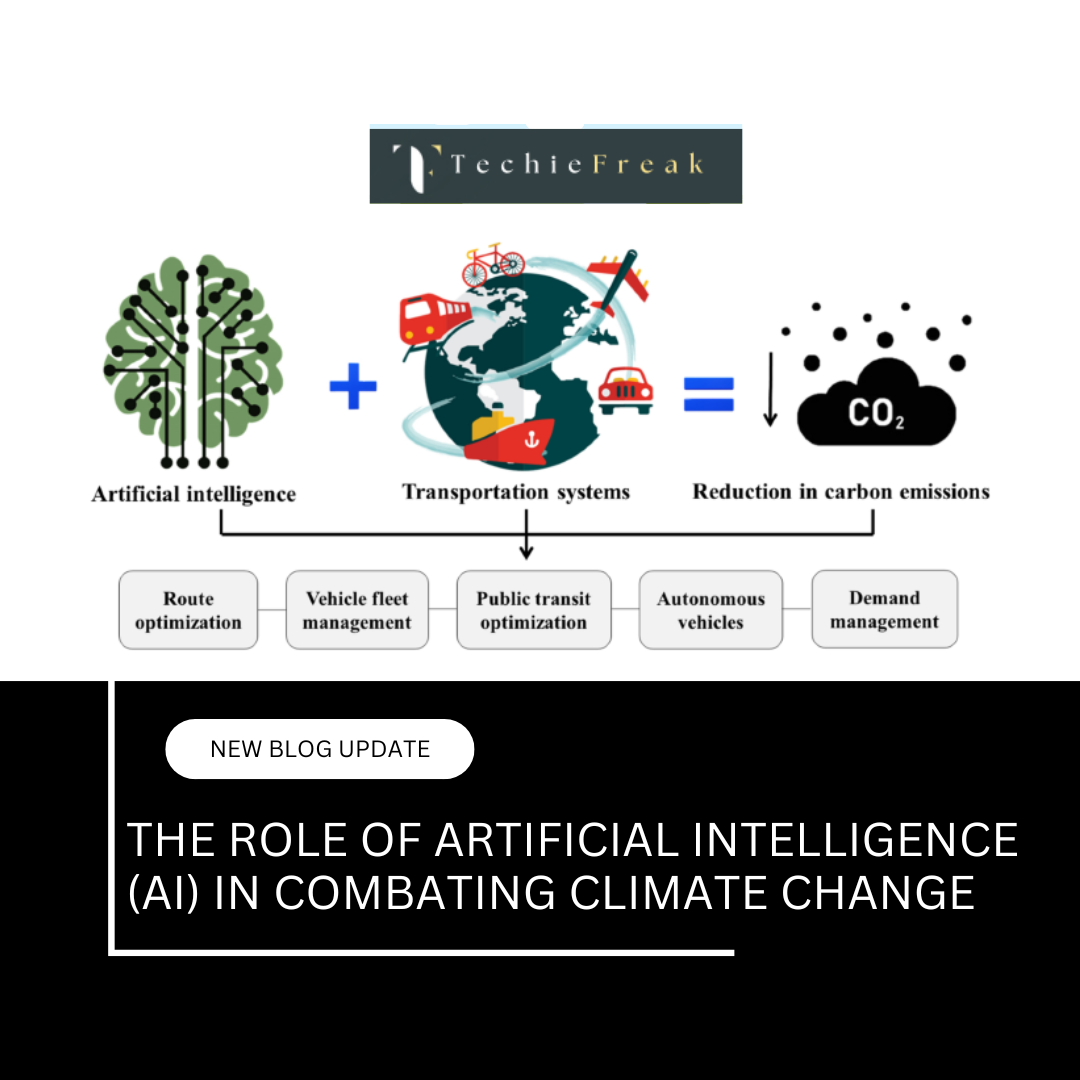
Next Blog- The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Combating Climate Change



.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)