The Role of Regulations in AI
1. Introduction: The Importance of Regulating AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly being integrated into various sectors such as healthcare, education, finance, criminal justice, and transportation. While it offers immense potential, the rapid adoption of AI has raised significant ethical, legal, and societal concerns. These include issues such as algorithmic bias, lack of transparency, misuse of personal data, and accountability for harmful outcomes.
In this context, regulation plays a critical role in guiding the development and deployment of AI technologies to ensure that they align with societal values, protect human rights, and mitigate risks.
2. Objectives of AI Regulation
AI regulations aim to achieve several key objectives:
a. Protecting Fundamental Rights
AI systems should not infringe upon fundamental rights such as privacy, equality, freedom of expression, or protection from discrimination. Regulations ensure that AI development respects these rights.
b. Ensuring Accountability
AI systems can make autonomous decisions. It is important to establish clear lines of accountability to determine who is responsible when systems fail, behave unexpectedly, or cause harm.
c. Promoting Transparency and Explainability
Regulations demand that AI systems, particularly those used in sensitive applications, are explainable and interpretable. Users and regulators must be able to understand how decisions are made.
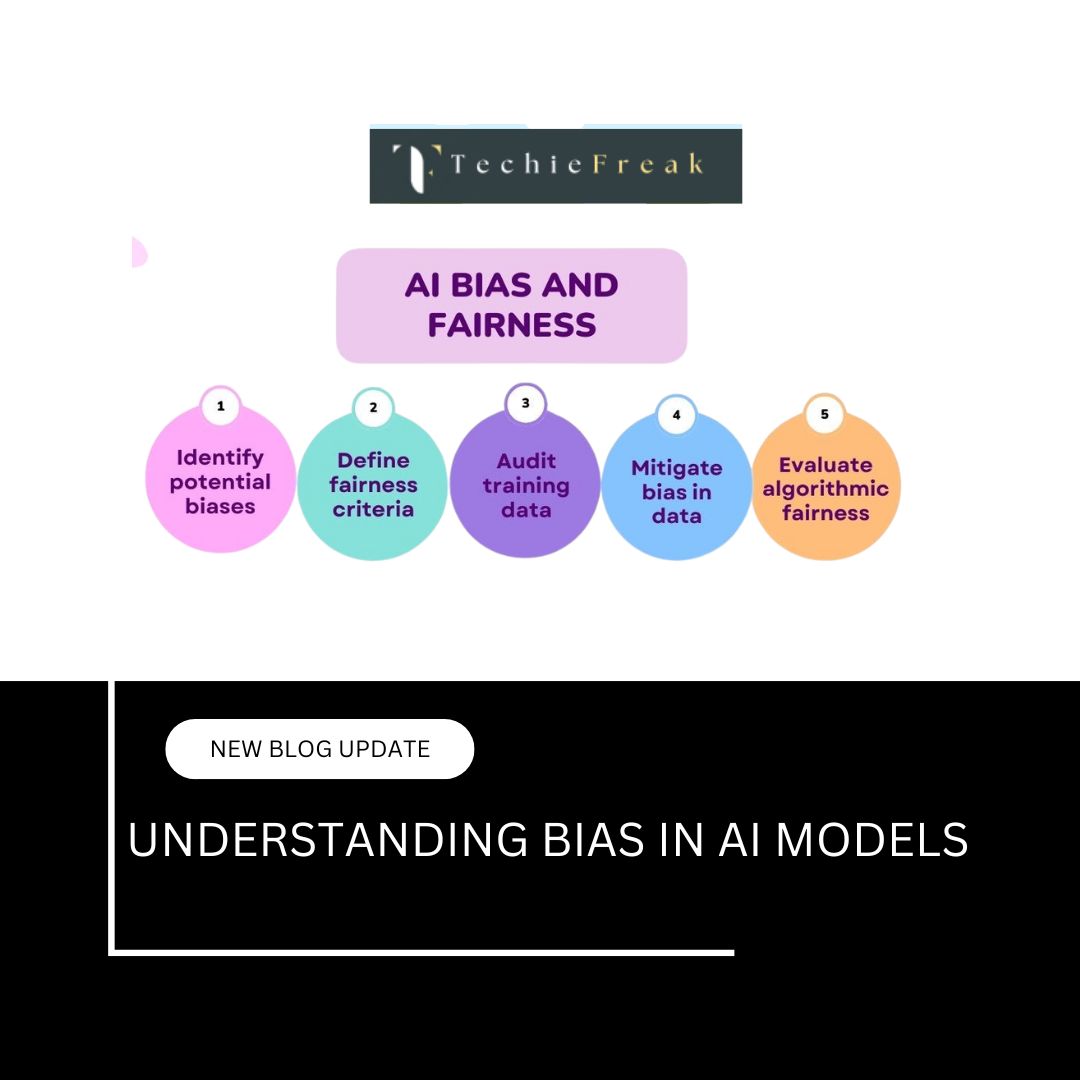
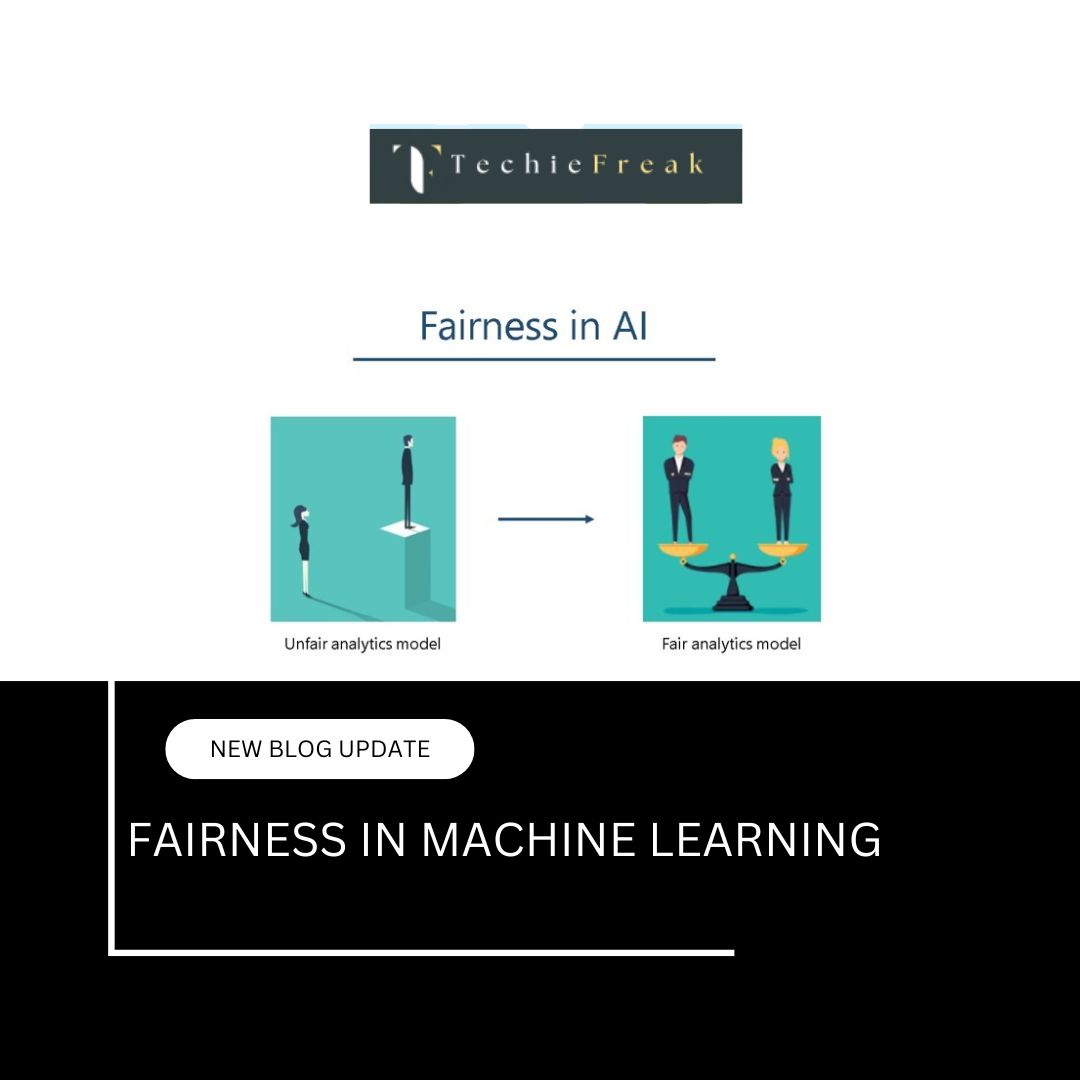
d. Reducing Bias and Discrimination
Regulatory frameworks help ensure that AI models are trained on representative datasets and do not reproduce or amplify existing societal biases.
e. Enhancing Safety and Security
AI systems must operate safely and securely to prevent unintended behavior or malicious exploitation.
f. Encouraging Trustworthy Innovation
Regulations help build public trust by ensuring that innovation in AI adheres to ethical standards and legal requirements.
3. Domains of AI Regulation
The following domains are typically addressed in AI regulatory frameworks:
a. Data Protection and Privacy
Given that AI relies heavily on large datasets, regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union enforce strict requirements on data collection, consent, anonymization, and user control over personal data.
b. Non-discrimination and Fairness
AI systems used in hiring, lending, law enforcement, or healthcare must be designed to treat all individuals fairly and not produce biased outcomes. Regular testing, auditing, and diverse training datasets are often mandated.
c. Human Oversight and Autonomy
AI should augment human decision-making, not replace it entirely. Regulations often require that human oversight is integrated into AI systems, especially in high-stakes applications.
d. Transparency and Explainability
Regulations may require AI developers to provide clear documentation of how systems work, what data is used, and how outcomes are determined, especially in cases affecting human rights.
e. Accountability and Liability
Laws must clearly define who is responsible when AI systems cause harm — the developers, the deployers, or the data providers. This ensures that victims have legal recourse.
f. Cybersecurity and System Robustness
AI regulations often include provisions for ensuring that AI systems are secure against hacking and function reliably under a wide range of conditions.
4. Comparative Overview of Global AI Regulatory Approaches
a. European Union (EU)
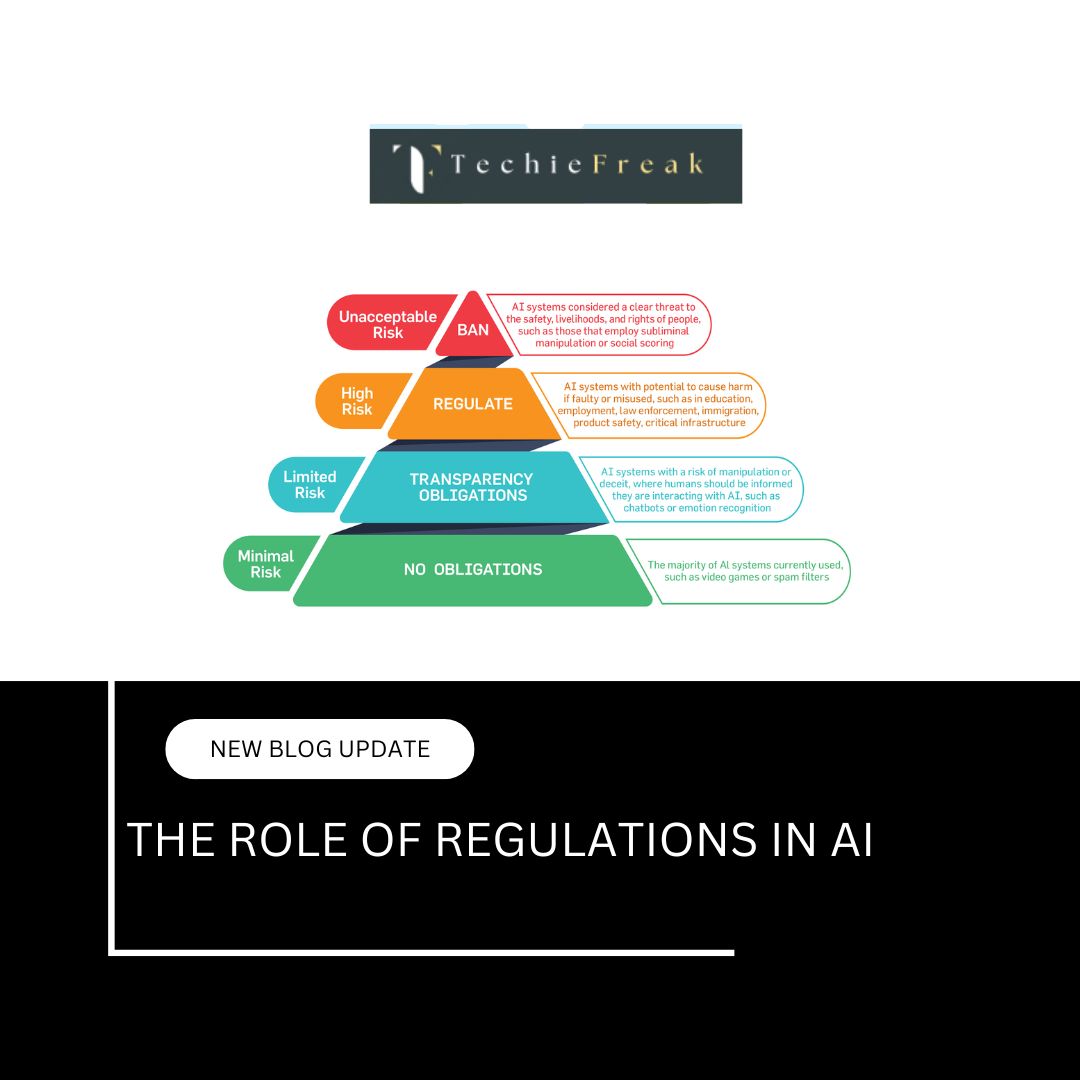
The EU has proposed a comprehensive Artificial Intelligence Act, which is currently under review. It is a risk-based framework that categorizes AI systems into four risk levels:
- Unacceptable Risk: These systems are considered a threat to safety or fundamental rights and are prohibited. Examples include social scoring systems and real-time facial recognition in public spaces.
- High Risk: These include AI systems used in critical infrastructure, education, employment, law enforcement, and medical devices. Developers must comply with strict requirements including data governance, documentation, risk assessment, and human oversight.
- Limited Risk: These systems require transparency obligations. For example, users must be informed when interacting with AI-driven chatbots.
- Minimal Risk: These systems, such as spam filters and video games, face no regulatory restrictions due to their low risk.
The EU AI Act emphasizes principles of transparency, accountability, and human rights protection. It also promotes innovation through regulatory sandboxes for startups and SMEs.
b. United States
The United States has adopted a decentralized and sector-specific approach. There is no federal AI regulation as yet, but various government agencies have issued guidance:
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) warns against biased or deceptive AI practices under consumer protection laws.
- In 2022, the White House released the Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights, which outlines five guiding principles:
- Safe and effective systems
- Algorithmic discrimination protections
- Data privacy
- Notice and explanation
- Human alternatives and fallback options
Different states and sectors (e.g., financial services, healthcare) have their own rules regarding algorithmic accountability and data use.
c. China
China’s approach to AI regulation is more centralized and aligned with state priorities. It mandates:
- Algorithms must promote "positive values" and avoid content that may cause instability.
- Companies must submit certain algorithms for review by government authorities.
- Strong controls on recommendation systems, facial recognition, and deep synthesis technologies.
The focus is on national security, political stability, and content moderation.
d. India
India is in the early stages of AI regulation. It does not have a dedicated AI law, but relevant aspects are covered under general IT laws and the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023.
The government think tank NITI Aayog has issued ethical guidelines advocating for responsible AI, focusing on inclusiveness, safety, and transparency.
India is also considering sector-specific norms and collaborative efforts through public-private partnerships to ensure ethical AI development.
5. Challenges in Regulating AI
a. Rapid Technological Advancements
The speed at which AI technologies evolve often outpaces legislative and regulatory processes. Laws may become outdated quickly.
b. Global Jurisdiction and Cross-border Applications
AI systems frequently operate across national boundaries. This raises questions about jurisdiction, enforcement, and harmonization of legal standards.
c. Definitional Ambiguities
There is no universally agreed-upon definition of AI. This makes it difficult to draft precise legislation and classify systems accurately.
d. Enforcement and Compliance
Regulators may lack the technical expertise or resources to effectively audit complex AI systems or detect non-compliance.
e. Balancing Innovation and Oversight
Overregulation may hinder technological innovation and economic growth. Conversely, under-regulation may lead to societal harm.
6. Industry Self-Regulation and Voluntary Standards
In addition to government regulations, many technology companies are adopting internal ethical guidelines and best practices. These include:
- Establishing ethics review boards
- Conducting bias audits
- Publishing model cards and system documentation
- Developing tools for fairness, explainability, and robustness
- Participating in multi-stakeholder initiatives and standardization bodies (e.g., ISO, IEEE)
However, self-regulation is not a substitute for legal oversight. It needs to be complemented by external accountability mechanisms.
7. Future Trends in AI Regulation
- Development of global AI governance frameworks, similar to climate or trade treaties.
- Adoption of real-time AI audits and automated compliance checks.
- Introduction of certification systems for AI applications, similar to safety or quality standards.
- Increased emphasis on public participation in shaping AI policy, especially in democratic societies.
- Implementation of AI impact assessments as a precondition for deployment in sensitive domains.
8. Conclusion
The regulation of AI is essential to ensure that the technology serves the interests of society and does not violate fundamental rights. As AI systems become more integrated into decision-making processes, it is crucial to develop robust, adaptable, and internationally harmonized regulatory frameworks.
Such frameworks should be guided by ethical principles such as fairness, accountability, transparency, and human oversight. The collaboration of governments, industries, civil society, and international organizations will be critical in shaping a responsible AI future.



.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)