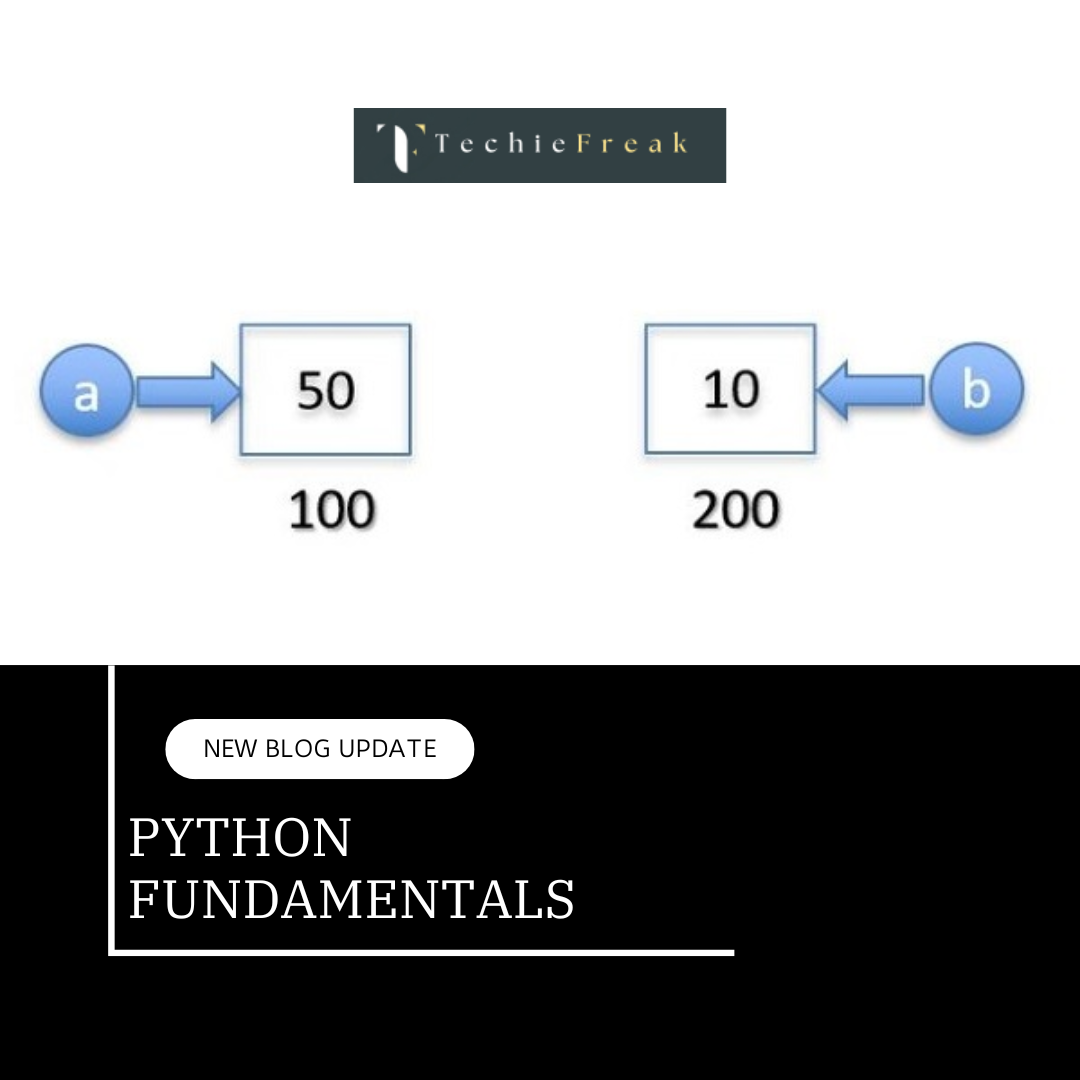
Operators are special symbols or keywords that perform operations on variables or values. Python has several types of operators categorized by their function.
Types of Operators in Python:
Operator Type | Purpose | Examples |
| Arithmetic Operators | Perform basic mathematical operations | +, -, *, / |
| Comparison Operators | Compare two values and return True or False | ==, !=, >, < |
| Logical Operators | Combine multiple conditions | and, or, not |
| Assignment Operators | Assign values to variables | =, +=, -=, *= |
| Bitwise Operators | Perform bit-level operations | &, ` |
| Membership Operators | Check if a value exists in a sequence | in, not in |
| Identity Operators | Check if two objects are the same in memory | is, is not |
Arithmetic Operators
These are used for performing mathematical calculations.
Operator | Description | Example |
| + | Addition | 3 + 5 = 8 |
| - | Subtraction | 10 - 4 = 6 |
| * | Multiplication | 6 * 3 = 18 |
| / | Division (float result) | 15 / 2 = 7.5 |
| // | Floor Division | 15 // 2 = 7 |
| % | Modulus (remainder) | 10 % 3 = 1 |
| ** | Exponentiation | 2 ** 3 = 8 |
Example:
a = 10
b = 3
print(a + b) # Output: 13
print(a // b) # Output: 3 (floor division)
print(a ** b) # Output: 1000 (10 raised to the power of 3)
Comparison Operators
These compare two values and return a boolean (True or False).
Operator | Description | Example |
| == | Equal to | 5 == 5 → True |
| != | Not equal to | 5 != 4 → True |
| > | Greater than | 7 > 3 → True |
| < | Less than | 3 < 5 → True |
| >= | Greater than or equal | 8 >= 8 → True |
| <= | Less than or equal | 2 <= 3 → True |
Example:
x = 10
y = 5
print(x > y) # Output: True
print(x == y) # Output: False
Logical Operators
These are used to combine multiple conditions.
Operator | Description | Example |
| and | True if both conditions are true | (5 > 3) and (4 > 2) → True |
| or | True if at least one is true | (5 > 3) or (2 > 4) → True |
| not | Reverses the condition | not (5 > 3) → False |
Example:
a = True
b = False
print(a and b) # Output: False
print(a or b) # Output: True
print(not a) # Output: False
Assignment Operators
These are used to assign values to variables.
Operator | Description | Example |
| = | Assign value | x = 5 |
| += | Add and assign | x += 3 (same as x = x + 3) |
| -= | Subtract and assign | x -= 2 |
| *= | Multiply and assign | x *= 4 |
Example:
x = 10
x += 5 # Same as x = x + 5
print(x) # Output: 15
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators work on binary (bit-level) representations of integers. They allow you to manipulate data at the level of 0s and 1s.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | AND: Sets each bit to 1 if both bits are 1. | 5 & 3 → 1 |
| ^ | XOR: Sets each bit to 1 if the bits are different. | 5 ^ 3 → 6 |
| ~ | NOT: Inverts all the bits. (Unary operator) | ~5 → -6 |
| << | Left Shift: Shifts bits left by a specified number of positions (adds 0s). | 5 << 2 → 20 |
| >> | Right Shift: Shifts bits right by a specified number of positions. | 5 >> 2 → 1 |
Examples:
# Binary: 5 → 0101, 3 → 0011
result = 5 & 3
print(result) # Output: 1 (Binary: 0001)
Membership Operators
Check if a value exists in a sequence (like a list, string, or tuple).
Operator | Description | Example |
| in | Value is in the sequence | 'a' in 'apple' → True |
| not in | Value is not in the sequence | 'z' not in 'apple' → True |
Example:
text = "Python"
print('P' in text) # Output: True
print('z' not in text) # Output: True
Identity Operators
Identity operators check whether two objects are the same object in memory, not just whether their values are the same.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| is | Returns True if two variables reference the same object in memory. | a is b |
| is not | Returns True if two variables reference different objects in memory. | a is not b |
Examples:
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = a # Both point to the same object
print(a is b) # Output: True
By mastering these foundational concepts, you’re setting yourself up for success in Python programming and beyond. Keep practicing with real-world examples to solidify your understanding!
Next Blog : Control Flow in Python



.png)









.png)

.png)