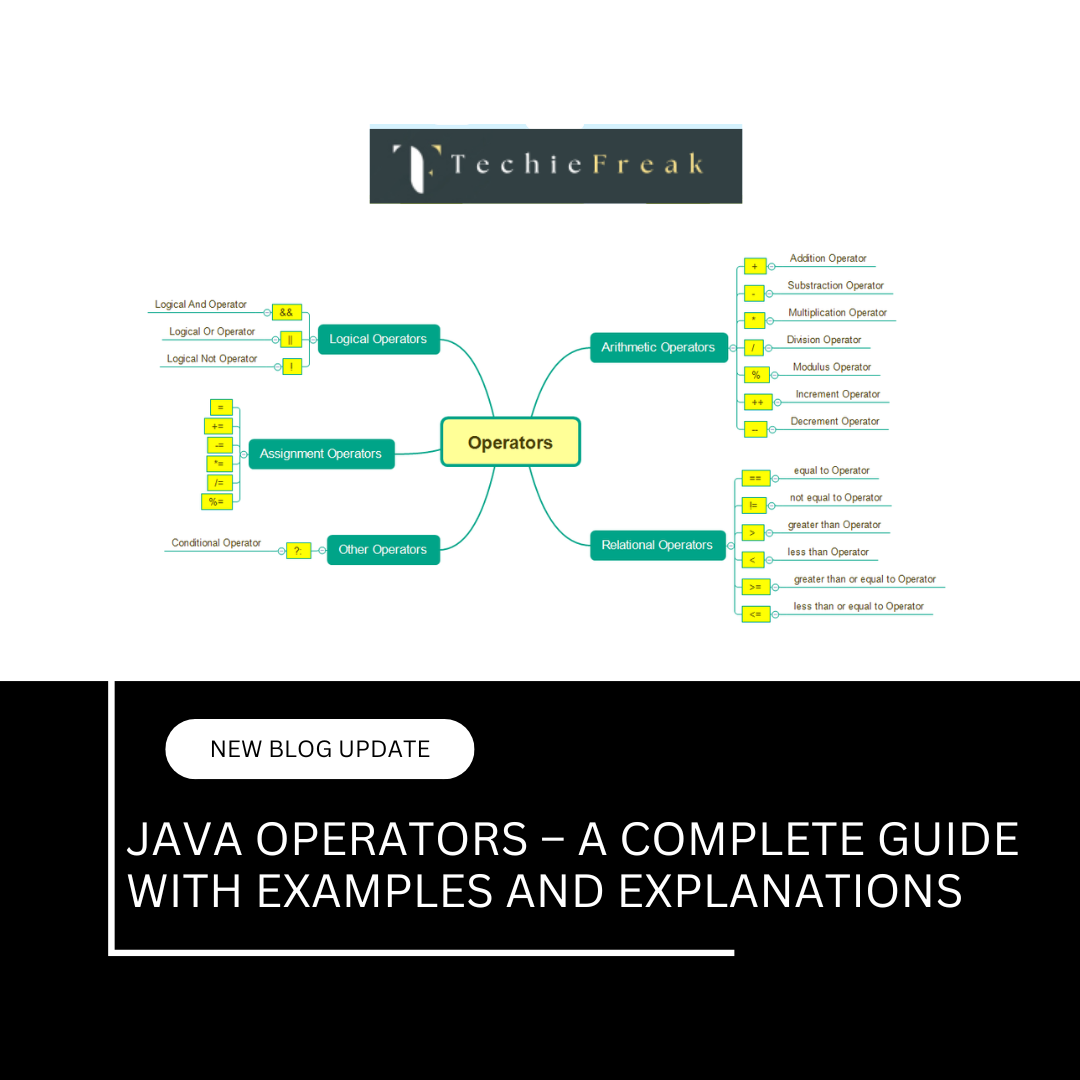
Java Operators – A Complete Guide with Examples and Explanations
Operators are symbols that instruct the compiler to perform specific mathematical, relational, or logical operations. They are fundamental to any programming language and are used extensively to manipulate data and control program flow.
In Java, operators are categorized based on the type of operation they perform. These include:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational (Comparison) Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Ternary (Conditional) Operator
Let’s go through each of these in detail, with both theory and well-explained examples.
1. Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators perform basic mathematical operations. These are used when you want to add, subtract, multiply, divide, or find the remainder of numeric values.
| Operator | Operation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | Adds two operands |
| - | Subtraction | Subtracts second operand from the first |
| * | Multiplication | Multiplies both operands |
| / | Division | Divides numerator by denominator |
| % | Modulus | Returns remainder of division |
Example:
int a = 15, b = 4;
System.out.println("Addition: " + (a + b)); // 19
System.out.println("Subtraction: " + (a - b)); // 11
System.out.println("Multiplication: " + (a * b));// 60
System.out.println("Division: " + (a / b)); // 3
System.out.println("Modulus: " + (a % b)); // 3
Explanation:
- a + b adds 15 and 4.
- a / b performs integer division; fractional part is discarded.
- a % b returns the remainder when 15 is divided by 4.
2. Relational Operators
Relational operators are used to compare two values or expressions. These comparisons result in a boolean value: true or false.
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal to | 5 == 5 | true |
| != | Not equal to | 5 != 3 | true |
| > | Greater than | 10 > 8 | true |
| < | Less than | 5 < 3 | false |
| >= | Greater than or equal | 5 >= 5 | true |
| <= | Less than or equal | 4 <= 3 | false |
Example:
int x = 10, y = 20;
System.out.println(x == y); // false
System.out.println(x != y); // true
System.out.println(x > y); // false
System.out.println(x <= y); // true
Explanation:
- x == y checks equality (false because 10 ≠ 20).
- x != y checks inequality (true because 10 ≠ 20).
- These are especially useful in conditions and loops.
3. Logical Operators
Logical operators combine multiple boolean expressions and return a boolean result. They’re commonly used in decision-making constructs.
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| && | Logical AND | Returns true if both conditions are true |
| || | Logical OR | Returns true if at least one of its operands evaluates to true. |
| ! | Logical NOT | Reverses the boolean value |
Example:
int age = 25;
System.out.println(age > 18 && age < 60); // true
System.out.println(age < 18 || age > 65); // false
System.out.println(!(age > 18)); // false
Explanation:
- &&: true because both conditions are true.
- ||: false because both conditions are false.
- !: negates the result of the condition.
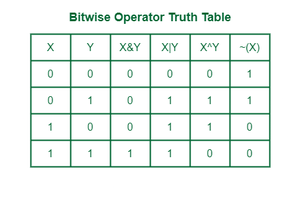
4. Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators perform operations on the individual bits of integer types. They're useful in low-level programming like device drivers and performance-sensitive applications.
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| & | AND | Performs bitwise AND |
| | | OR | Performs a logical OR operation on each corresponding bit of two operands. |
| ^ | XOR | Performs bitwise exclusive OR |
| ~ | NOT | Performs bitwise NOT (inverts bits) |
| << | Left Shift | Shifts bits to the left (multiply by 2) |
| >> | Right Shift | Shifts bits to the right (divide by 2) |
_1753290880.png)
Example:
int a = 5, b = 3;
System.out.println("a & b: " + (a & b)); // 1
System.out.println("a | b: " + (a | b)); // 7
System.out.println("a ^ b: " + (a ^ b)); // 6
System.out.println("~a: " + (~a)); // -6
System.out.println("a << 1: " + (a << 1));// 10
System.out.println("a >> 1: " + (a >> 1));// 2
Explanation:
- 5 in binary: 0101, 3: 0011
- &: 0101 & 0011 = 0001 (1)
- |: 0101 | 0011 = 0111 (7)
- ^: 0101 ^ 0011 = 0110 (6)
- ~a: Inverts bits and returns -6 (in 2’s complement)
5. Assignment Operators
Assignment operators assign values to variables. Apart from the standard =, Java supports combined operators that perform an operation and assignment together.
| Operator | Description | Equivalent Expression |
|---|---|---|
| = | Assign | a = 10 |
| += | Add and assign | a = a + 5 |
| -= | Subtract and assign | a = a - 5 |
| *= | Multiply and assign | a = a * 2 |
| /= | Divide and assign | a = a / 2 |
| %= | Modulus and assign | a = a % 2 |
Example:
int a = 10;
a += 5; // a = 15
a *= 2; // a = 30
a -= 10; // a = 20
System.out.println("Final value: " + a); // 20
Explanation:
These make code shorter and cleaner by reducing redundancy in arithmetic operations followed by assignments.
6. Ternary Operator (Conditional Operator)
The ternary operator is a shorthand for if-else statements and is often used to assign values based on a condition.
Syntax:
variable = (condition) ? valueIfTrue : valueIfFalse;
Example:
int age = 18;
String result = (age >= 18) ? "Eligible" : "Not Eligible";
System.out.println(result);
Explanation:
- If the condition age >= 18 is true, "Eligible" is assigned to result, otherwise "Not Eligible" is assigned.
Summary Table
| Category | Operators | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic | +, -, *, /, % | Basic math operations |
| Relational | ==, !=, >, <, >=, <= | Comparison, returns boolean values |
| Logical | &&,||, ! | To combine multiple boolean expressions or to negate a boolean condition. |
| Bitwise | &, | , ^, ~, <<, >> | Perform operations at the binary level, manipulating individual bits of integer values. |
| Assignment | =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %= | Assign and modify values |
| Ternary | condition ? expr1 : expr2 | Short form of if-else |
Final Thoughts
Operators allow you to manipulate data and control your program logic. Understanding them well helps you write powerful and expressive Java code. Practice combining different types of operators to build dynamic expressions.
Next Blog- Java Control Flow Statements



 Basics.png)