Tree Bins in Java: What They Are and How They Work
1. Introduction
In Java’s ConcurrentHashMap (Java 8 and later), tree bins are an advanced internal optimization designed to improve lookup performance when there are many hash collisions.
They replace the traditional linked list structure for hash buckets with a balanced tree when a bin becomes too large.
This blog explains what tree bins are, why they exist, and how they work internally.
2. What Is a Tree Bin?
A tree bin is a bin (bucket) inside a hash table that stores its entries as a balanced binary search tree, rather than a simple linked list.
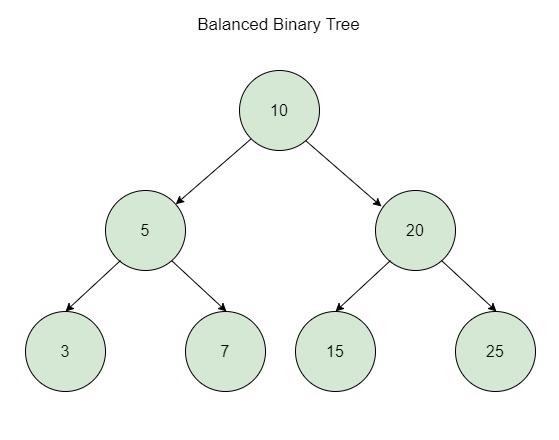
When too many keys hash to the same bucket, lookup performance in a linked list degrades to O(n).
By converting such a bucket to a balanced tree (specifically a red-black tree), lookups improve to O(log n) for that bucket.
3. Why Tree Bins Exist
Hash collisions are inevitable because of finite bucket counts and imperfect hash functions.
If collisions are frequent, linked lists inside bins grow long, causing slow lookups and insertions.
Java 8’s ConcurrentHashMap uses tree bins to:
- Reduce lookup time for high-collision bins.
- Maintain consistent performance even with poor hash distributions.
- Improve scalability for large datasets.
4. When Does a Bin Become a Tree?
In Java 8’s ConcurrentHashMap, a bin is transformed into a tree if:
- The number of entries in that bin exceeds a threshold (TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, usually 8).
- The overall table size is large enough (at least MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY, usually 64 buckets).
If the table is too small, instead of treeifying, the table is resized to reduce collisions.
5. How Tree Bins Work

Step-by-Step:
- Normal Bin (Linked List):
Initially, each bin contains entries linked as a list. Each entry has a hash, key, value, and pointer to the next entry. - Collision Threshold Reached:
If the number of entries in a bin exceeds TREEIFY_THRESHOLD (usually 8), Java converts that bin to a tree bin. - Red-Black Tree Creation:
A balanced red-black tree is created, where:- Nodes are sorted by hash value.
- Each node stores a key-value pair and pointers to child nodes.
- Tree balancing rules ensure that the tree depth is minimized.
- Operations on Tree Bin:
- Search: O(log n) complexity.
- Insertion/Removal: O(log n) complexity with rebalancing as needed.
6. Advantages of Tree Bins
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Faster lookup | From O(n) to O(log n) when collisions are high |
| Better scalability | Efficient performance even for poor hash codes |
| Reduced memory footprint | Compared to extremely long linked lists in collision-heavy bins |
7. Example: Conceptual Tree Bin Structure
Hash Table
+--------------------------------------------+
| Bin 0 -> Linked List |
| Bin 1 -> Tree Bin (Red-Black Tree) |
| Bin 2 -> Linked List |
| Bin 3 -> Tree Bin |
+--------------------------------------------+
Tree Bin Example (Bin 1):
[Hash: 23]
/ \
[Hash: 15] [Hash: 42]
/ \ / \
... ... ... ...
8. Pseudo-Code
if (bin.size() >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) {
if (table.length >= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) {
convertBinToTree(bin);
} else {
resizeTable();
}
}
Here:
- TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8
- MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64
This ensures treeification only happens when it truly improves performance.
9. How Tree Bins Are Implemented in Java
In Java 8’s ConcurrentHashMap, tree bins are implemented as TreeBin containing TreeNode instances.
Each TreeNode stores:
- Key
- Value
- Hash
- Pointers to left and right child nodes
- Parent pointer
- Color (red or black for balancing rules)
Java uses Red-Black tree algorithms to maintain balance after insertions or deletions.
10. When Tree Bins Are Converted Back to Linked Lists
If the number of entries in a tree bin falls below a certain threshold (UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD, usually 6), the bin is converted back to a linked list to avoid unnecessary complexity for small bins.
11. Performance Comparison
| Structure | Lookup Complexity |
|---|---|
| Linked List | O(n) |
| Tree Bin | O(log n) |
Tree bins guarantee stable performance even in high-collision scenarios.
12. Summary
Tree bins are one of the most important optimizations introduced in Java 8’s ConcurrentHashMap.
By converting high-collision buckets into balanced trees:
- Lookup and update performance improves dramatically.
- The system becomes more scalable and resilient to poor hash functions.
Key takeaways:
- Tree bins only occur when collisions exceed a threshold.
- They use red-black tree structures for balancing.
- They are converted back to linked lists if entries fall below a certain threshold.
 (56).png)
 (17).png)
.png)
 (53).png)
 (18).png)

.png)
.png)
 (1).png)
 (2).png)
 (3).png)
 (4).png)
 (5).png)
 (6).png)
 (9).png)
 (7).png)
 (10).png)
 (8).png)
 (10).png)
 (12).png)
 (13).png)
 (13).png)
 (15).png)
 (16).png)
 (19).png)
 (20).png)
 (21).png)
 (22).png)
 (23).png)
 (24).png)
 (25).png)
 (26).png)
 (27).png)
 (28).png)
 (29).png)
 (30).png)

 (31).png)
 (32).png)
 (54).png)
 (33).png)
 (34).png)
 (35).png)
 (36).png)
 (37).png)
 (38).png)
 (39).png)
 (40).png)
 (41).png)
 (42).png)
 (45).png)
 (46).png)
 (47).png)
 (48).png)
 (55).png)
 (50).png)
 (51).png)
 (52).png)
.png)
 (44).png)
