Find the Average of Array Elements
Problem Statement
Given an array of numbers, the task is to find the average (mean) of all elements in the array.
The average of an array is calculated using the formula:
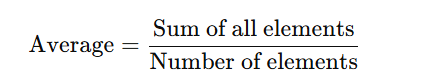
Why This Problem Is Important
This problem introduces and reinforces:
- Array traversal
- Accumulating values using loops
- Division and type handling
- Difference between integer and floating-point results
It is widely used in:
- Statistical calculations
- Data analysis
- Performance metrics
- Real-world scoring and grading systems
Input and Output Format
Input
Array: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
Output
Average = 30
Key Points to Remember
- Always calculate the sum first
- Divide by the total number of elements
- Be careful with integer division in some languages
- Use floating-point data types when needed
Approach / Logic
- Initialize sum = 0
- Traverse the array and add each element to sum
- Count the number of elements (n)
- Compute average = sum / n
- Print the average
Step-by-Step Algorithm
- Start
- Read the array and its size
- Initialize sum = 0
- Loop through the array
- Add each element to sum
- Divide sum by n
- Print the average
- End
Pseudocode
sum = 0
n = length of array
for i = 0 to n-1:
sum = sum + arr[i]
average = sum / n
print average
Dry Run Example
Array = [4, 6, 8, 10]
sum = 0
sum = 0 + 4 → 4
sum = 4 + 6 → 10
sum = 10 + 8 → 18
sum = 18 + 10 → 28
n = 4
average = 28 / 4 = 7
Time and Space Complexity
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Time Complexity | O(n) |
| Space Complexity | O(1) |
Only one traversal is required, and no extra space is used.
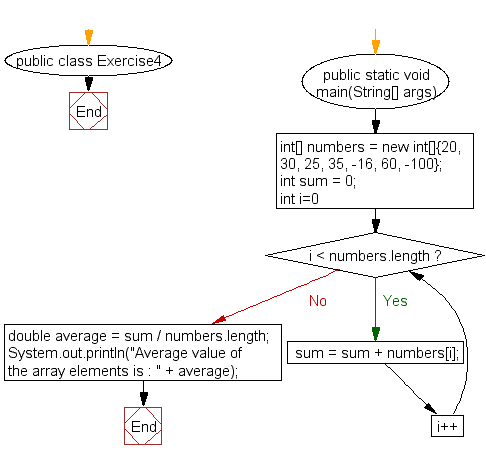
Language-wise Implementation
C Implementation
#include
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
float average = (float)sum / n;
printf("Average of array elements: %.2f", average);
return 0;
}
Output
Average of array elements: 30.00
C++ Implementation
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
double average = (double)sum / n;
cout << "Average of array elements: " << average;
return 0;
}
Output
Average of array elements: 30
Java Implementation
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int sum = 0;
for(int num : arr) {
sum += num;
}
double average = (double) sum / arr.length;
System.out.println("Average of array elements: " + average);
}
}
Output
Average of array elements: 30.0
Python Implementation
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
sum_elements = 0
for num in arr:
sum_elements += num
average = sum_elements / len(arr)
print("Average of array elements:", average)
Output
Average of array elements: 30.0
C# Implementation
using System;
class Program {
static void Main() {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int sum = 0;
foreach(int num in arr) {
sum += num;
}
double average = (double) sum / arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Average of array elements: " + average);
}
}
Output
Average of array elements: 30
JavaScript Implementation
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
let average = sum / arr.length;
console.log("Average of array elements:", average);
Output
Average of array elements: 30
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using integer division unintentionally
- Forgetting to type-cast before division
- Dividing before summing all elements
- Not handling empty arrays (in advanced cases)
Interview Variations
- Average of even elements only
- Average of elements at even indices
- Running average of array
- Average in a given range
Detailed Summary
Finding the average of array elements is a foundational problem that combines array traversal, accumulation, and arithmetic operations. By summing all values and dividing by the total number of elements, we compute a meaningful statistical measure. This problem emphasizes careful handling of data types, especially in languages where integer division can lead to incorrect results. Mastery of this concept is essential for progressing to more complex problems involving statistics, prefix sums, and real-time data analysis.
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
