Transformers in NLP: The Revolution of AI-Language Models
Introduction
In recent years, transformer-based models have revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP), enabling machines to understand and generate human-like text with remarkable accuracy. Unlike earlier sequence models such as Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs), transformers rely on a mechanism called self-attention, allowing them to process entire sentences in parallel while capturing long-range dependencies and context.
This article explores:
- How transformers transformed NLP
- Key transformer models: BERT, GPT, and T5
- Code implementation using the Hugging Face Transformers library
How Transformers Revolutionized NLP
Transformers have significantly transformed the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) by overcoming limitations in previous models like RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks) and LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory networks). This guide explores:
- The challenges of traditional NLP models
- How transformers solve these problems
- Key innovations like self-attention, positional encoding, and parallel processing
Challenges in Traditional NLP Models
1. Sequential Processing in RNNs and LSTMs
- Problem: RNNs process text word-by-word in a sequential manner, meaning each word depends on the previous ones.
- Issue: This makes training slow and prevents parallel processing, limiting scalability.
- Example:
If we process the sentence “The cat sat on the mat” using an RNN, it must first understand "The", then "cat", then "sat", and so on. - Why this is inefficient:
- Long sentences slow down computation.
- Harder to leverage modern GPU architectures, which excel in parallel computing.
2. Difficulty Handling Long-Range Dependencies
- Problem: RNNs and LSTMs struggle to capture long-range dependencies in text.
Example:
In the sentence:"The professor, who was known for his groundbreaking research in artificial intelligence, received a prestigious award."
- A traditional RNN might forget that "professor" is the subject when it reaches "received".
- This is called the vanishing gradient problem, where the model forgets important earlier information.
- LSTMs improved this using gates, but still faced limitations for extremely long sentences.
3. Lack of Bidirectional Understanding
- Problem: Traditional models often process text left to right (or right to left), leading to incomplete context understanding.
- Example:
Consider the sentence:
"The bank on the river was crowded."
- If a model reads "The bank on the river", it might still be uncertain whether "bank" refers to a financial institution or a riverbank.
- The rightward processing might not capture enough context.
Solution:
- Bidirectional models like BERT (based on transformers) can understand context from both directions, improving accuracy.
How Transformers Solved These Challenges
1. Self-Attention Mechanism
The self-attention mechanism allows a model to weigh different words in a sentence based on their relevance, without relying on sequential processing.
How does it work?
- Instead of processing words one-by-one, a transformer compares each word with every other word in the sentence.
- It assigns attention scores to determine which words are important.
Example:
In the sentence:
"The cat, despite being scared, jumped over the dog."
A self-attention mechanism ensures that:
- "jumped" pays more attention to "cat" rather than "dog", even though "dog" is closer in position.
- This is done by assigning higher weights to relevant words.
Mathematically, self-attention works using:
- Query (Q) → Represents the word being analyzed.
- Key (K) → Represents the other words being compared.
- Value (V) → Represents the word’s meaning.
- Attention Scores → Computed using dot product and softmax functions.
Why is Self-Attention Important?
- Captures long-range dependencies
- Understands contextual meaning
- Computes relationships between words efficiently
2. Positional Encoding
Since transformers do not process words sequentially, they need a way to retain word order information.
Positional encodings solve this by adding unique numerical patterns to each word.
Example:
Consider the sentences:
"She loves coffee." vs. "Coffee loves her."
- Without word order, both sentences might appear similar.
- Positional encoding ensures the model understands their difference.
Mathematical Representation
Each word is assigned a vector based on its position:
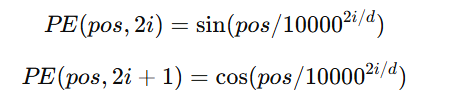
Where:
- pos is the position of the word in the sentence
- i is the dimension index
- d is the embedding size
This encoding helps transformers distinguish word order without needing sequential processing.
3. Parallel Processing
Unlike RNNs, which process text sequentially, transformers handle entire text sequences at once.
Advantages of Parallel Processing:
- Faster training by leveraging GPUs
- Better scalability for large datasets
- No vanishing gradient problem, unlike RNNs
Example:
If given the sentence:
"The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."
- A transformer can process all words simultaneously, instead of going word by word.
- This makes training much more efficient compared to RNNs.
Key Transformer Models in NLP
Transformers have revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP), leading to the development of powerful models like BERT, GPT, and T5. Each of these models has distinct architectures and training strategies tailored for different NLP tasks.
This guide provides an in-depth look at:
- The architecture of these models
- How they work
- Their applications in real-world scenarios
1. BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)
Overview
Developed by Google, BERT is a bidirectional transformer model designed to understand the full context of a word by looking at both preceding and following words. This overcomes the limitations of traditional models, which process text either left-to-right or right-to-left, missing crucial contextual relationships.
How BERT Works
1. Masked Language Modeling (MLM)
- Instead of predicting the next word in a sentence (like GPT), BERT masks some words randomly and trains the model to predict them based on surrounding words.
- This forces BERT to understand bidirectional context, unlike traditional models that only consider past words.
Example:
"The [MASK] sat on the mat."
- BERT learns that the missing word could be "cat" based on surrounding context.
2. Next Sentence Prediction (NSP)
- Helps BERT understand relationships between sentences, improving performance in tasks like question answering and summarization.
- During training, BERT is given two sentences, and it must predict whether the second follows the first.
Example:
- Sentence 1: "The weather is nice today."
- Sentence 2: "Let's go for a walk."
- BERT predicts whether Sentence 2 is logically related to Sentence 1.
Applications of BERT
- Search Engines: Google uses BERT to enhance search results by understanding query intent better.
- Question Answering: Models trained on datasets like SQuAD provide more accurate answers.
- Sentiment Analysis: Helps in customer feedback analysis and brand monitoring.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifies entities like names, places, and organizations in text.
2. GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
Overview
Developed by OpenAI, GPT is a unidirectional (left-to-right) transformer that excels in text generation. Unlike BERT, which focuses on understanding text, GPT is designed to generate human-like responses based on a given prompt.
How GPT Works
1. Causal Self-Attention
- Unlike BERT, which processes words in both directions, GPT only looks at previous words when predicting the next word.
- This prevents it from "cheating" by seeing future words in a sentence.
Example:
"The cat sat on the [MASK]"
- GPT predicts "mat" only using the context before the masked word.
2. Pre-training and Fine-tuning
- Pre-training: GPT is trained on massive datasets to learn grammar, reasoning, and facts.
- Fine-tuning: It is later fine-tuned on specific tasks like summarization, chatbots, or coding assistance.
Applications of GPT
- Conversational AI: Powers chatbots like ChatGPT and virtual assistants.
- Content Creation: Used for blog writing, script generation, and storytelling.
- Code Generation: Helps developers with GitHub Copilot and OpenAI Codex.
- Summarization & Paraphrasing: Converts lengthy documents into concise summaries.
3. T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer)
Overview
T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) is a deep learning model developed by Google that treats every NLP task as a text-to-text problem. This means that regardless of the task—summarization, translation, question answering, or classification—both input and output are represented as text.
This approach is different from:
- BERT, which is primarily designed for understanding text (e.g., classification, named entity recognition).
- GPT, which is designed for text generation (e.g., chatbots, creative writing).
- T5, which combines both understanding and generation in a unified framework.
How T5 Works
1. Text-to-Text Framework
- Every NLP task is formatted as input text → output text.
- The model does not have separate architectures for different tasks.
Examples:
| Task | Input Format | Output Format |
|---|---|---|
| Summarization | "Summarize: The article discusses the impact of AI in healthcare..." | "AI improves diagnostics and patient care." |
| Translation | "Translate English to French: The weather is nice today." | "Le temps est agréable aujourd'hui." |
| Question Answering | "Question: Who discovered gravity? Context: Isaac Newton formulated the laws of motion." | "Isaac Newton" |
2. Pre-training on the C4 Dataset
The Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus (C4) is the dataset used to pre-train T5. It is derived from a large-scale web scraping of publicly available text.
What is the C4 Dataset?
- C4 is a filtered version of the Common Crawl dataset (which contains huge amounts of text from the internet).
- Google researchers cleaned and processed this dataset to remove spam, duplicate content, and non-English text.
- It is much larger and more diverse than traditional NLP datasets (e.g., Wikipedia or news articles).
- Since it contains text from a variety of domains, T5 learns a broad knowledge base and adapts well to different NLP tasks.
Why Use C4 for Pre-training?
- Diverse Text Sources – Covers various domains such as news, blogs, scientific articles, and books.
- Scalability – Provides an extensive dataset for training large-scale transformer models.
- Better Generalization – Helps the model understand language patterns across different contexts.
Pre-training Process in T5
Like many modern NLP models, T5 undergoes two key stages:
1. Pre-training (Self-Supervised Learning)
- T5 is initially trained on a masked language modeling task called "Span Corruption".
- Instead of masking single words (like BERT), T5 removes entire spans of text and asks the model to reconstruct them.
- Example:
- Input: "The impact of [MASK] in medicine is significant."
- Expected Output: "AI"
This method helps T5 understand long-range dependencies in language.
2. Fine-Tuning (Task-Specific Training)
- After pre-training, the model is fine-tuned on specific NLP tasks (e.g., summarization, sentiment analysis, machine translation).
- This allows T5 to adapt to specialized use cases while retaining its general knowledge from pre-training.
Key Advantages of T5
- Unified Model for Multiple NLP Tasks – Unlike BERT and GPT, which specialize in specific types of tasks, T5 can handle both text understanding and generation in a single model.
- Pre-trained on a Large Corpus (C4) – Makes it highly adaptable to various domains.
- State-of-the-Art Performance – Outperforms many existing models on NLP benchmarks such as GLUE, SuperGLUE, and SQuAD.
Applications of T5
- Text Summarization: Used in news aggregation and document processing.
- Machine Translation: Converts text between multiple languages efficiently.
- Question Answering: Powers AI assistants and FAQ systems.
- Document Understanding: Helps businesses analyze contracts, reports, and research papers.
Comparison: BERT vs. GPT vs. T5
| Feature | BERT | GPT | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developer | OpenAI | ||
| Training Direction | Bidirectional | Unidirectional (left-to-right) | Text-to-text format |
| Main Goal | Understanding text | Generating text | Both understanding & generating |
| Pre-training Tasks | MLM, NSP | Causal self-attention | Text-based task conversion |
| Common Uses | Search engines, NER, QA | Chatbots, content creation | Summarization, translation |
Implementing Transformers with Hugging Face
Hugging Face provides an easy-to-use Transformers library, allowing developers to implement and fine-tune transformer models for various NLP tasks like text classification, translation, question answering, and more.
This guide explains:
- Installing dependencies
- Using pre-trained BERT for text classification
- How the model works under the hood
- Fine-tuning BERT for custom datasets
1. Installing Dependencies
To use Hugging Face’s transformers library, you need to install the following packages:
pip install transformers torch
- transformers: Provides pre-trained transformer models.
- torch: Required for running models based on PyTorch.
2. Using Pre-trained BERT for Text Classification
Step 1: Load a Sentiment Analysis Pipeline
Hugging Face provides pipelines, which are pre-configured models for different NLP tasks.
We can load a BERT-based sentiment analysis model with just a few lines of code.
from transformers import pipeline
# Load a sentiment analysis pipeline using a pre-trained BERT model
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
# Test the model on a sample text
text = "I love learning about transformers!"
result = classifier(text)
# Print the output
print(result)
Output:
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998}]
- The model correctly identifies positive sentiment in the text.
- The confidence score (0.9998) indicates a high certainty of the classification.
3. How the Model Works Under the Hood
1. Tokenization (Text to Numbers)
Transformer models cannot process raw text. Instead, the text is converted into tokens (numerical representations).
Hugging Face uses the WordPiece tokenizer, which:
- Splits words into subwords if they are rare (e.g., "transformers" → "transform", "##ers").
- Adds special tokens like [CLS] (start of sentence) and [SEP] (end of sentence).
Example of tokenization:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
tokens = tokenizer("I love learning about transformers!", return_tensors="pt")
print(tokens)
Output (Tokenized Text)
{'input_ids': tensor([[101, 1045, 2293, 4083, 2055, 19081, 2015, 999, 102]]),
'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])}
- input_ids: Encoded word tokens.
- attention_mask: Indicates which tokens should be attended to (1 = valid token, 0 = padding).
2. BERT Model Processing
- The tokenized input is passed through a pre-trained BERT model.
- BERT generates hidden state embeddings for each token.
- The [CLS] token's embedding is passed to a fully connected layer for classification.
3. Classification Output
- The final layer outputs probabilities for each sentiment class (POSITIVE or NEGATIVE).
- The class with the highest probability is selected.
4. Fine-tuning BERT on a Custom Dataset
If you want to train BERT on your own dataset, you need:
- A labeled dataset (text + sentiment labels).
- A pre-trained BERT model to fine-tune.
- The Trainer API from Hugging Face.
Example: Fine-tuning BERT for Custom Sentiment Analysis
Step 1: Load Dataset
Let's assume you have a dataset in CSV format with text and label columns.
import pandas as pd
from datasets import Dataset
# Load dataset from a CSV file
df = pd.read_csv("custom_sentiment_data.csv")
# Convert to Hugging Face Dataset format
dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(df)
Step 2: Preprocess the Data
We need to tokenize the text before passing it to BERT.
def tokenize_data(example):
return tokenizer(example["text"], truncation=True, padding="max_length", max_length=512)
# Apply tokenization to the dataset
dataset = dataset.map(tokenize_data)
Step 3: Load Pre-trained BERT Model
We load a BERT model for classification (bert-base-uncased) with a classification head on top.
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
# Load BERT model for text classification
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", num_labels=2)
- num_labels=2 because we are doing binary classification (Positive/Negative).
- If dealing with multiple sentiment classes, update num_labels accordingly.
Step 4: Define Training Arguments
We use Hugging Face’s Trainer API to train the model.
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./results",
evaluation_strategy="epoch",
save_strategy="epoch",
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
num_train_epochs=3,
logging_dir="./logs",
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=dataset["train"],
eval_dataset=dataset["test"],
)
Step 5: Train the Model
trainer.train()
- This fine-tunes BERT on your dataset.
- After training, the model can classify custom sentiment data accurately.
5. Making Predictions with a Fine-Tuned Model
Once fine-tuned, use the model for predictions.
# Load the fine-tuned model
fine_tuned_classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis", model="path_to_your_model")
# Test on new text
result = fine_tuned_classifier("The movie was amazing!")
print(result)
6. Performance Considerations
1. Hardware Acceleration
- Running transformer models requires high computational power.
- If using Google Colab, enable GPU acceleration (Runtime → Change runtime type → Select GPU).
- If using a local machine, consider CUDA-enabled GPUs with PyTorch for faster inference.
2. Optimizing Model Performance
- Use DistilBERT (lighter version of BERT) for faster inference.
- Quantization reduces model size while maintaining accuracy (torch.quantization).
- Batch processing improves efficiency when making multiple predictions.
7. Summary
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Install transformers and torch |
| 2 | Load a pre-trained BERT-based sentiment classifier |
| 3 | Tokenize input text |
| 4 | Pass tokens through BERT to get predictions |
| 5 | Fine-tune BERT on a custom dataset |
| 6 | Use the trained model for custom predictions |
By leveraging Hugging Face’s Transformers library, we can quickly build state-of-the-art NLP models with minimal effort.
Key Takeaways
Transformer-based models like BERT, GPT, and T5 have revolutionized NLP by enabling deeper contextual understanding, efficient processing, and high-quality text generation. While BERT is great for understanding text, GPT excels at generating human-like responses, and T5 unifies multiple NLP tasks into a single framework.
With the rise of AI-powered applications like Google Search (BERT), ChatGPT (GPT), and AI-assisted translation (T5), transformers continue to push the boundaries of what machines can achieve in human language understanding. Learning how to implement and fine-tune these models will be crucial for advancing NLP applications in the future.
Next Blog- Building Chatbots with NLP
.png)



.jpg)









.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)